Machinery and equipment play a vital role in coal mine production, once the failure will directly affect the normal operation of coal mining enterprises, and in serious cases, it may cause casualties. Gears and bearings are the transmission parts with the highest failure rate, so it is of great practical significance to carry out fault diagnosis research on them. At present, the main methods for fault diagnosis of gears and bearings in coal mining machinery include ferrographic analysis, noise analysis and vibration analysis. Compared with ferrographic analysis and noise analysis, the use of vibration analysis to diagnose faults has the advantages of convenience, timeliness and effectiveness, and can be monitored in real time
Measure the operating status of gears and bearings, so as to achieve early detection and early maintenance, and avoid major safety accidents. Based on this, vibration analysis is used to diagnose gear and bearing faults. The vibration analysis method is further divided into two types: time domain method and frequency domain method.
1 Fault types and causes of coal mine machinery gears and bearings
1.1 Gears
The gear has the advantages of light weight, small size, high transmission accuracy, good reliability and the ability to withstand heavy loads. All kinds of coal mining machinery and equipment often use gear transmission to work. However, various faults often occur in the transmission process of gears, which affect the accuracy of transmission and lead to the absence of equipment
The law is in normal service. Gear failures include flank wear, flank pitting, and flank gluing
3 types. (1) Tooth surface wear refers to the involute tooth profile in the process of gear transmission
Relative slippage occurred. Severe tooth flank wear can lead to involute tooth distortion, resulting in large impact and noise, and even gear breakage. The fault is mainly caused by the large friction and high working intensity of the gear working surface. The gears in coal mining machinery and equipment are prone to tooth surface wear during the transmission process. Prolonged service aggravates the degree of wear,
This in turn causes the gear to fail.
(2) Tooth surface pitting refers to the small pits formed by the hard contact of the gear surface caused by fatigue cracks, and with the expansion of cracks. If the hardness of the material used to manufacture the gear is insufficient, it is easy to cause pitting corrosion in the actual service process.
(3) Tooth surface gluing is the adhesive or tear marks formed on the relatively soft tooth surface. Choosing a lubricating oil with a high viscosity can effectively prevent the occurrence of such failures. The power of coal mining machinery and equipment is usually relatively large, and it is easy to cause the internal temperature to be too high under the condition of heavy load, high speed and insufficient lubrication of the tooth surface, resulting in the failure of tooth surface gluing.
1.2 Bearings
Bearing is the core component of coal mining machinery and equipment, if it fails in the service process, it will cause the equipment to stop running, resulting in serious economic losses. The main types of bearing failures are wear, fatigue, cracking, corrosion and cracking. In the actual operation process, the bearing is subjected to large alternating changes Load, it is easy to cause spalling cracks on the surface, and eventually cause fatigue damage. Acids and alkalis will corrode the bearing if they invade the inside of the bearing, and the continuous expansion of the corrosion area will cause corrosion failures. In the harsh coal mining environment, due to the poor sealing, some hard fine particles will enter the bearing, causing local damage. If it is not detected and solved in time, the high-speed operation of the bearing will cause wear failure.
2 Fault diagnosis method and diagnosis process of coal mine machinery gears and bearings
2.1 Fault diagnosis methods
2.1.1 Time Domain Law
The time-domain method is a method that directly analyzes the collected vibration signals of gears and bearings to achieve fault diagnosis. When the gears and bearings of coal mining machinery fail, the time-domain vibration waveform will change, and the characteristic quantity of the signal can be extracted for diagnosis. Compared with other fault diagnosis methods, the time-domain waveform is the original fluctuation of the acquisition, which contains rich fault information. At present, the commonly used time-domain waveform characteristic indexes include mean, variance, kurtosis, margin, and pulse. However, due to various factors such as vibration signal acquisition equipment and the acquisition environment, the collected time-domain signal often contains a lot of noise sound, so that the weak fault information is masked by the noise. Therefore, when using the time-domain method for fault diagnosis, it is necessary to adopt a scientific and effective way to reduce noise, so as to better extract weak fault information and improve the accuracy of fault diagnosis. The time-domain method is used to carry out the coal mine machinery gear and The key to bearing fault diagnosis lies in the selection of characteristic quantities, and the accuracy of fault diagnosis is relatively low, which is not suitable for dealing with the early failure of gears and bearings.
2.1.2 Frequency domain approach
The frequency domain method converts the measured vibration signal into the frequency domain and analyzes the signal in the frequency domain, so as to effectively diagnose gear and bearing faults. Compared with the time-domain method, the fault diagnosis accuracy of the frequency-domain method is better
High. The theoretical basis of this method is the Fourier transform, and the resonance demodulation technique and cepstrupt spectrum analysis technology are often used. Before the frequency domain analysis, it is also necessary to reduce the noise of the measured vibration signal to improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
2.2 Troubleshooting process
The troubleshooting process for gears and bearings is similar. First of all, the fault diagnosis object is determined, and the vibration signal of the equipment is collected by arranging the accelerometer through the data acquisition equipment, and the data is integrated. Secondly, the corresponding data mining technology is used to extract the faults in the test signal Information. Data mining is crucial and directly affects the fault diagnosis of gears and bearings, so it must be done in a scientific and effective way. Finally, fault diagnosis is carried out, and the decision-making results are obtained through analysis to determine whether the gear and bearing are faulty. The troubleshooting process for gears and bearings is shown in Figure 1.
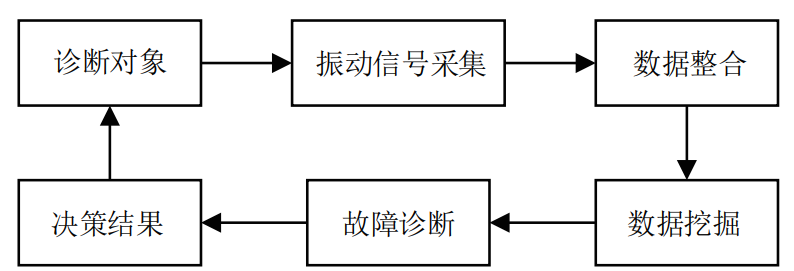
Figure 1 Troubleshooting process for gears and bearings
3 Example of bearing fault diagnosis
Taking bearing failure as an example, the specific application of the time-domain method and the frequency-domain method is analyzed. Since the bearing is a rotating part, the change of its fault signal is often periodic, and the theoretical fault frequency can be obtained through the speed and geometry of the bearing. The failure frequency of the inner ring of the rolling bearing is Fi, and the failure frequency of the outer ring The formulas for the rate fo, the rolling element failure frequency fr and the cage failure frequency fh are respectively
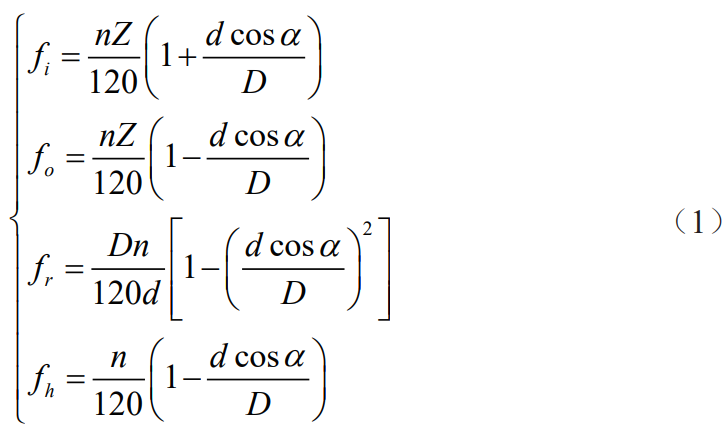
where :d is the diameter of the rolling element; D is the diameter of the bearing pitch circle; α is the contact angle; Z is the number of rolling elements; n is the rotational speed. Fault damage bearings are generally marked out with a certain width of fault single damage points on the working surface of the outer ring of the bearing, the working surface of the inner ring and the rolling element by the method of EDM. A deep groove ball bearing with model 6205-2RS JEM SKF was selected as the test object and the bearing under test was used as the support Motor shaft. The basic parameters of this bearing are: inner ring diameter of 25 mm, outer ring diameter of 52 mm, thickness of 15 mm, rolling element diameter of 7.94 mm, pitch diameter of 39.04 mm, sampling frequency of 12 kHz, motor speed of 1 772 r · min-1
。 The rolling bearing vibration test platform is shown in Figure 2 Shown is a 1.5 kW electric motor, torque sensor, power tester, and electronic controller that uses an accelerometer to collect vibration signals. Test bearings are divided into drive end bearings and fan end bearings. Accelerometers are mounted in the upper position of each of these two bearings.
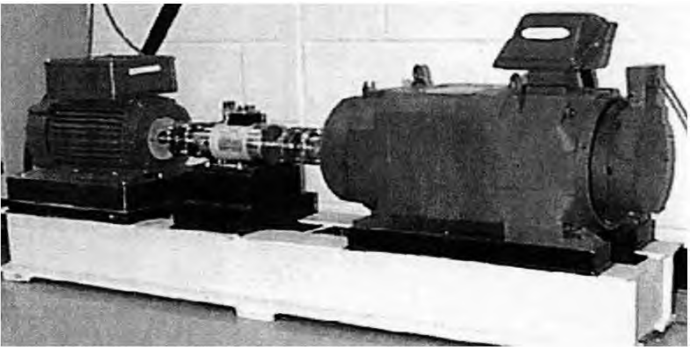
Figure 2 Rolling bearing vibration test platform
The rolling bearings used in this test are divided into 3 groups, which represent its 3 state modes, namely inner ring failure, outer ring failure and rolling element failure. The vibration signals of rolling bearings under different working conditions in three state modes were collected by the recorder, and the spectrum analysis of the collected signals was carried out. The results are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Results of time-frequency analysis of rolling bearing failures
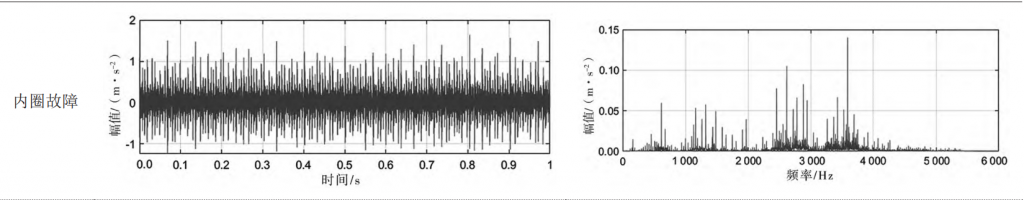
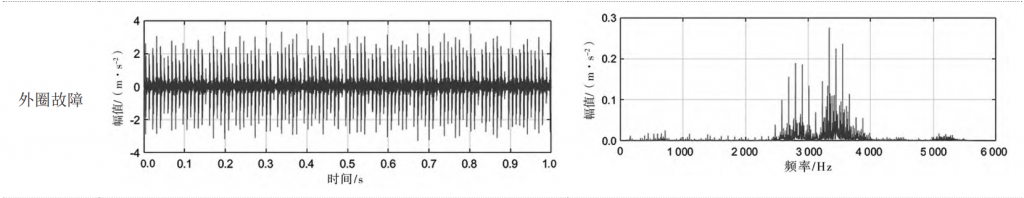
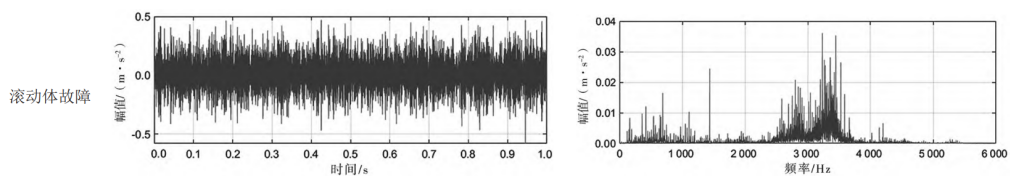
As can be seen from Table 1, the time-domain signals of the three faults are difficult to identify, while the frequency domain can accurately diagnose the type of bearing fault.
4 Conclusion
This paper analyzes the types and causes of the faults of gears and bearings of coal mining machinery, points out that vibration analysis method is an effective means for fault diagnosis, and diagnoses the fault of coal mining machinery bearings through specific examples. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, its application to the analysis of time domain signals and frequency domain signals can greatly improve the accuracy of fault diagnosis, which is essential for coal mining enterprises
It is of great significance to avoid major safety accidents in the normal production of the industry.
