Due to the advantages of low-pressure vacuum carburizing and high-pressure gas quenching heat treatment over traditional atmosphere carburizing in terms of carburizing accuracy, intergranular oxidation-free, Steel gears and control of part deformation, they have been widely used in the fields of automotive component manufacturing, machinery, and aerospace component manufacturing. The transmission system speed of new energy vehicles has been greatly increased compared to traditional fuel vehicles, reaching up to tens of thousands of revolutions. Therefore, higher requirements have also been placed on the accuracy and reliability of key components such as gears and bearings for new energy vehicles. An imported multi-heating chamber automated vacuum low-pressure carburizing production line is mainly used for the production of precision gear carburizing heat treatment for new energy vehicles within the factory. Its attached Infracarb process simulation system can simulate the number and duration of intense carburization and diffusion pulses based on the material properties and effective hardening layer depth requirements of the processed workpiece. Based on the different hardenability and quenching processes used in producing workpieces, the difference between the effective hardening layer depth detection results and simulated values is within 5%.
Hardness testing
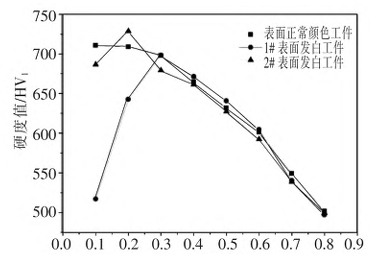
Surface hardness distribution curve of gear workpieces after heat treatment. The quenching temperature of workpiece 1# is 950℃, and the quenching temperature of workpiece 2# is 870℃.Steel gears For gear workpieces with normal surface color, the hardness gradually decreases with the increase of distance from the surface, and the hardness reduction rate is less than 40HV1/01mm. The hardness at a distance of 0.05mm from the surface is 710.5HV1, which is converted to Rockwell hardness of 60.2HRC, which meets the technical requirements. From the hardness curve of workpiece 1#, it can be seen that when the distance from the surface is not greater than 0.2mm, the hardness value is between 505 and 640HV1,Steel gears which is far lower than the technical requirement value of 660-750HV1; when the distance from the surface is greater than 0.2mm, the hardness distribution is very close to that of workpieces with normal surface color. Therefore, it can be seen that the hardness lower than normal value only exists in a very shallow region near the surface, which is called the “head-down” phenomenon. From the hardness curve of workpiece 2#, it can be seen that when the distance from the surface is not greater than 0.1mm, there is a “head-down” phenomenon in the hardness; when the distance from the surface is greater than 0.1mm, the hardness distribution shows a normal hardness gradient.
Abnormal Analysis and Discussion of Steel Gear Production Process
Through observing the whitening position of the 20CrMnTiH gear workpiece in multiple furnaces, it was found that the whitening position of the workpiece was toward the outside of the tooling.Steel gears The excessive amount of residual austenite on the tooth top angle and tooth surface of the gear is caused by the high concentration of saturated carbon. In order to find out the cause of the local high carbon concentration on the tooth surface of the products at both ends of the tooling, we analyzed the process parameters and carburizing quenching process records of related furnaces, and found no abnormalities. It is speculated that the equipment may cause local whitening of the products. The workpiece enters and exits the heating chamber through a transfer cart in the transfer channel, which is equipped with a heat shield with two open ends. After the carburizing process is completed, the internal transfer cart automatically opens and moves to the corresponding heating chamber to carry out the workpiece transfer. Then it is transferred to the gas quenching chamber. Due to the different distances between each heating chamber and the gas quenching chamber, the transfer time is 9-12 seconds. Leakage detection was conducted on the acetylene process pipeline between the heating chamber liner and water cooling wall, and multiple gas leakage points were found. When multiple heating chambers are working, acetylene enters the transfer channel through leakage points before entering the heating chamber. Due to the low pressure and temperature in the channel, the leaked acetylene will accumulate in the channel. Due to the accumulation of acetylene in the channel, after being discharged from the furnace, the workpiece at both ends of the tooling first comes into contact with the acetylene accumulated in the channel during the transfer process.Steel gears The high temperature workpiece will adsorb active carbon atoms decomposed from acetylene during the transfer process, forming secondary strong carburization in a short period of time. Due to high quenching temperature, after quenching, a large amount of residual austenite is generated on the surface layer, which also causes significant differences in microstructure between the residual austenite layer and the subsurface layer rather than a gradual trend with increasing depth. The presence of a large amount of residual austenite on the surface layer of the workpiece leads to a decrease in tooth surface hardness Low and gear contact fatigue strength is reduced. A large amount of residual austenite is generated on the tooth surface, which transforms under the action of grinding heat and grinding force during grinding, resulting in grinding cracks on the tooth surface and causing significant quality risks. Therefore, it is particularly necessary to ensure product quality and avoid acetylene leakage into the transfer channel through the pipeline. By repairing the acetylene leakage point, after multiple production observations, Steel gears no whitening phenomenon was found. Metallographic structure observation and hardness testing tracking on the workpieces at both ends of the tooling also found no abnormalities, ensuring product quality, reducing scrap rate, and creating good economic benefits for the enterprise.
Conclusion and Suggestion
The large amount of residual austenite on the surface of the 20CrMnTiH gear workpiece after secondary carburizing and quenching is the main cause of its local whitening and low surface hardness. Leak detection and repair improvements to the acetylene pipeline interface of the equipment have avoided excessive acetylene leakage into the transfer channel,Steel gears solving the problem of excessive residual austenite on the surface of the workpiece after quenching.
