1) Root crack and inner and outer raceway failure of bearing
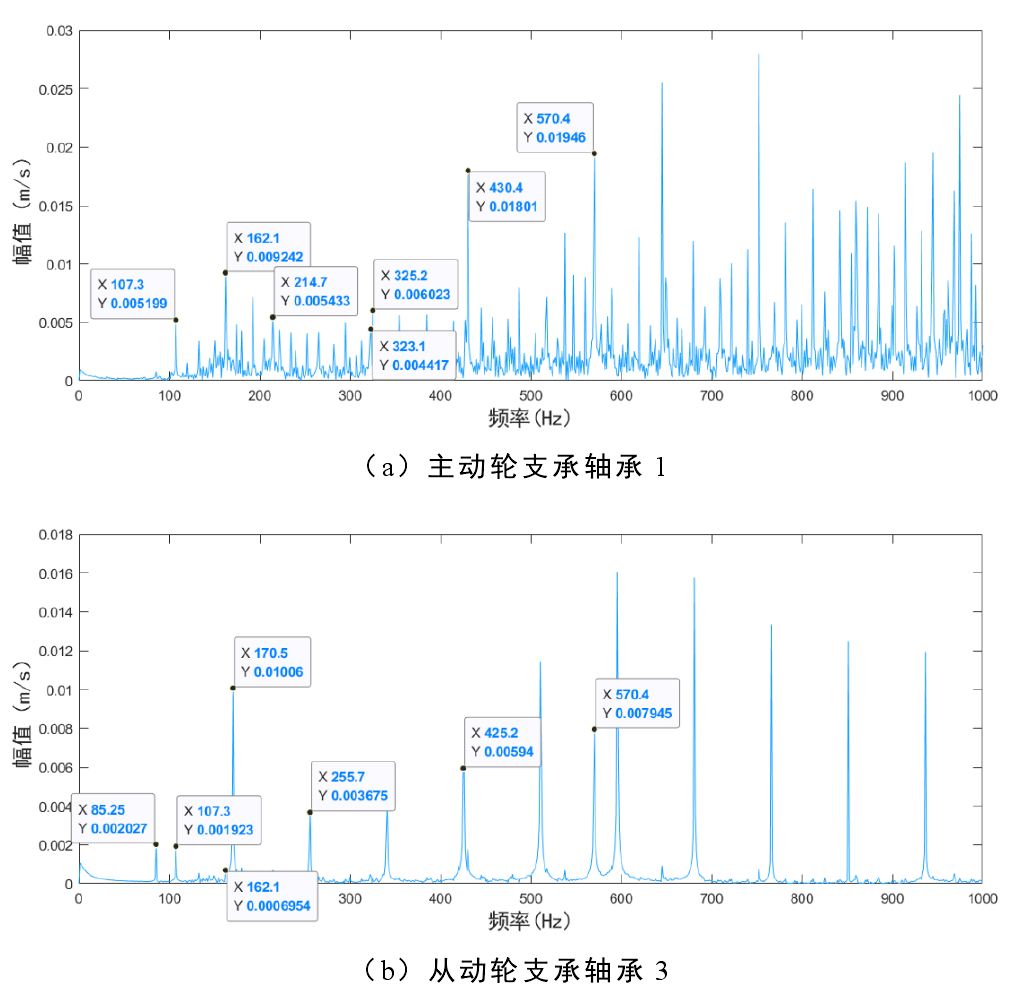
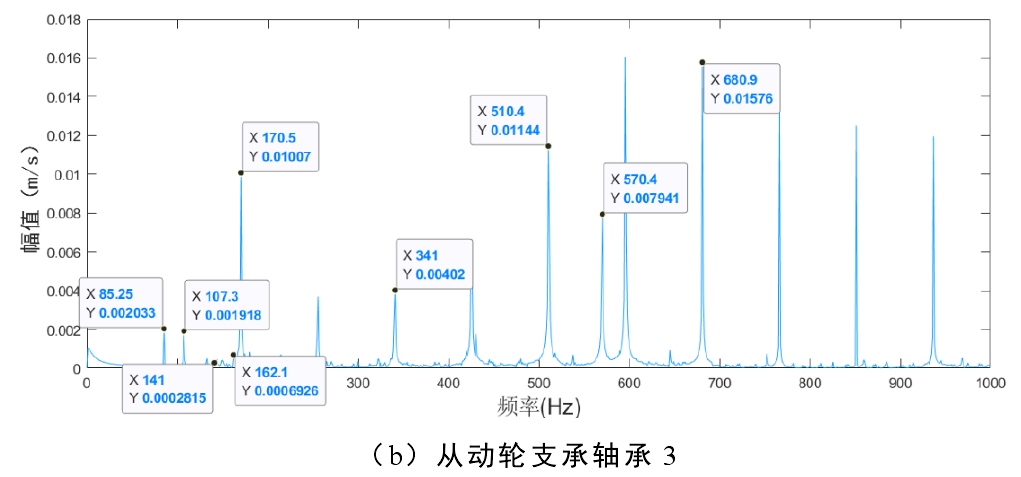
Figure 1 shows the frequency domain diagram of bearing 1 and bearing 3 when root crack and inner and outer raceway faults of bearing occur simultaneously. The main frequency components in Figure 1 (a) are: outer raceway fault frequency 𝑓o (107.3hz) and its multiple frequency, inner raceway fault frequency 𝑓i (162.1hz) and its multiple frequency and fault gear meshing frequency 𝑓m (570.4hz). The main frequency components in Figure 1 (b) are: double frequency 85.25hz of bearing 3 outer raceway fault frequency, 𝑓o (107.3hz) of bearing 1 outer raceway fault frequency, bearing 1 inner raceway fault frequency and fault gear meshing frequency. By comparing the two figures, it can be found that the frequency component of bearing 1 is obviously more than that of bearing 3. This is because the composite fault of bearing 1 and driving wheel causes more sidebands. The increase of frequency components can also reveal the generation of system fault to some extent.
2) Root crack, bearing outer raceway fault and rolling element fault

Fig. 2 shows the frequency domain diagram of bearing 1 and bearing 3 when root crack, rolling element fault and outer raceway fault occur simultaneously. The main frequency components of Figure 2 (a) are: outer raceway fault frequency 𝑓o (107.3hz) and its multiple frequency, double frequency of rolling element fault frequency 2𝑓b (141hz), fault gear meshing frequency 𝑓m (570.4hz). The main frequency components of Figure 2 (b) are: frequency doubling of bearing 3 outer raceway fault frequency, double frequency of rolling element fault frequency, bearing 1 outer raceway fault frequency and fault gear meshing frequency.
3) Root crack, inner raceway fault and rolling element fault
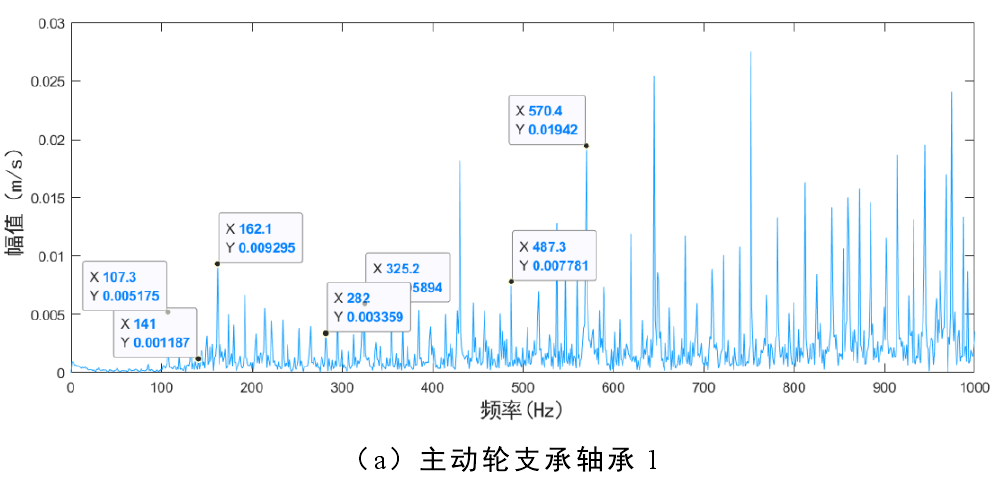
Fig. 3 shows the frequency domain diagram of bearing 1 and bearing 3 when root crack, rolling element fault and inner raceway fault occur simultaneously. The main frequency components of Figure 3 (a) are: double frequency 2𝑓b (141hz) of rolling element fault frequency, 𝑓i (162.1hz) of bearing 1 inner raceway fault frequency and fault gear meshing frequency 𝑓m (570.4hz). The main frequency components of Figure 3 (b) are: frequency doubling of bearing 3 outer raceway fault frequency, double frequency of bearing 1 rolling element fault frequency and other frequency doubling and meshing frequency of fault gear.
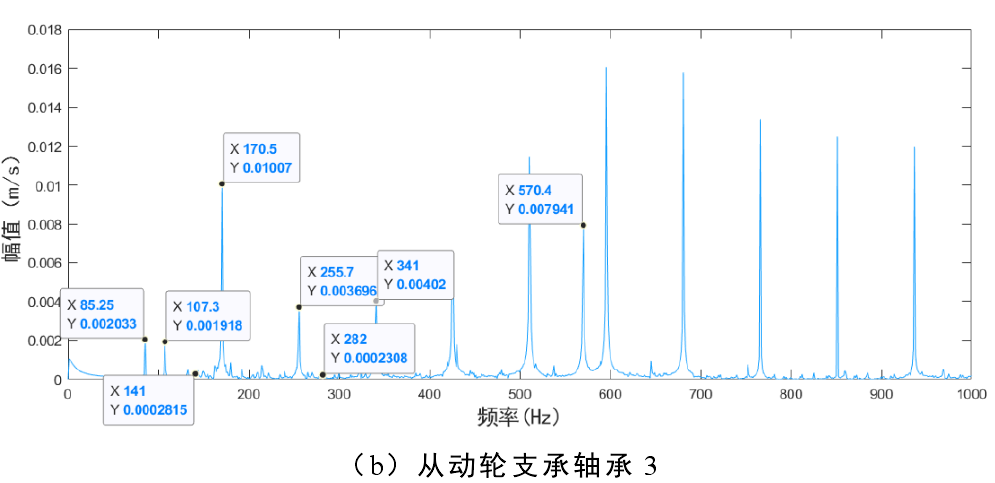
4) Root crack, inner and outer raceway fault of bearing and rolling element fault
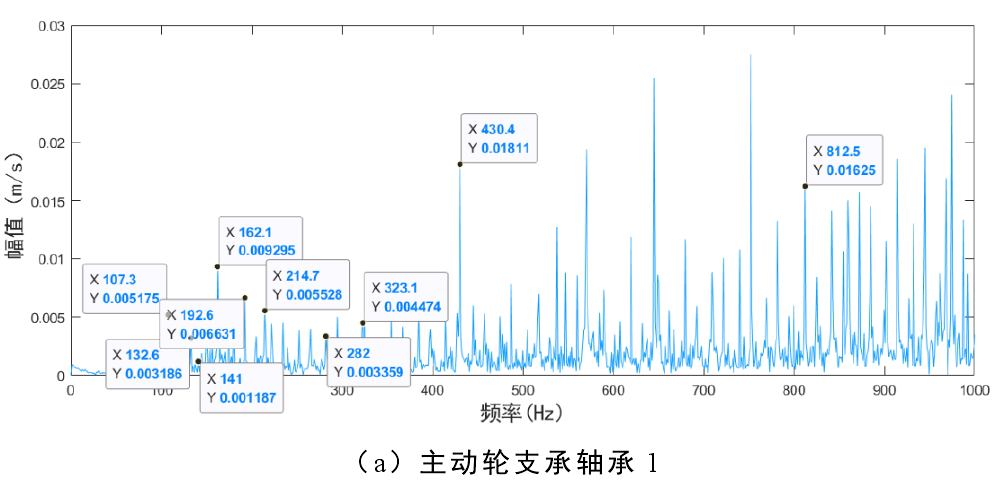
Fig. 4 shows the frequency domain diagram of bearing 1 and bearing 3 when root crack, rolling element fault and inner and outer raceway faults occur simultaneously. The main frequency components of Figure 4 (a) are: the second harmonic frequency of rolling element fault frequency 2𝑓b (141hz), bearing 1 inner raceway fault frequency 𝑓i (162.1hz) and its multiple frequency, outer raceway fault frequency 𝑓o (107.3hz) and its multiple frequency and fault gear meshing frequency 𝑓m (570.4hz). The main frequency components of Figure 4 (b) are: the frequency doubling of bearing 3 outer raceway fault frequency, bearing 1 outer raceway fault frequency, inner raceway fault frequency, rolling element fault frequency double frequency and fault gear meshing frequency.
Through the above analysis, it can be found that: the meshing frequency of the fault gear is very obvious, which can be easily found from the frequency domain diagram. The fault characteristic frequency of the outer raceway of the rolling bearing 1 always exists in each time domain diagram, while the amplitude of the fault characteristic frequency of the rolling element is relatively small, which is not easy to be found, and the characteristic frequency of the inner raceway is also obvious. Since bearing 1 is a fault bearing and bearing 3 is a healthy bearing, the fault characteristics of bearing 1 and gear can be found through the time domain diagram of bearing 3, which shows that the fault characteristic frequency can be transmitted between systems. In addition, it can be found that the outer raceway fault frequency of the bearing can be seen in each compound fault frequency, which is the vibration characteristics of the rolling bearing itself.
