The influence range of each installation deviation on fatigue parameters is shown in the figure. According to the order of influence range, the first is the cross angle installation deviation Gama value, the second is the offset distance installation deviation V value, the third is the axial installation deviation H value of the hypoid gear small wheel, and the last is the axial installation deviation g value of the hypoid gear large wheel. For the equivalent fatigue stress, the variation range of the large wheel of hypoid gear is larger than that of the small wheel of hypoid gear. Based on the above analysis, the following influence rules of bending fatigue stress of hypoid gears can be summarized:
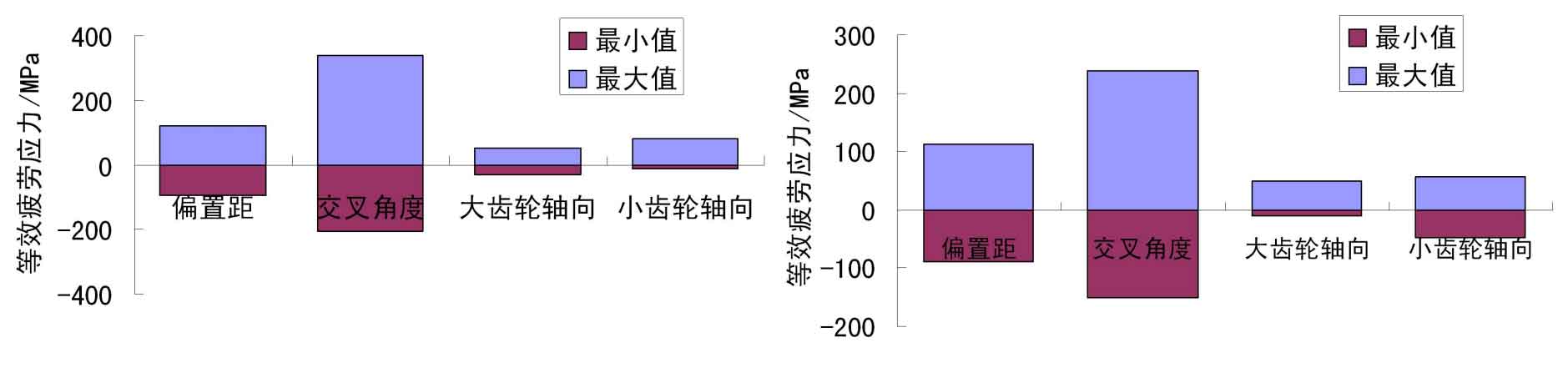
(1) When the parameters change in the same range, the installation cross angle of hypoid gear has the greatest influence on the equivalent fatigue stress of the tooth root. Because of the change of the intersection angle of the hypoid gears, the hypoid gears will appear edge contact, which causes the root fatigue stress of the hypoid gears to rise sharply; Secondly, the deviation of the installation offset distance will also cause the edge contact of the hypoid gear, which will increase the fatigue stress of the hypoid gear when it meshes in or out; Thirdly, it is the axial installation deviation of hypoid gear pinion. The axial installation deviation of hypoid gear pinion is not easy to cause the edge contact of hypoid gear, but it will lead to the increase of fatigue stress at the meshing middle position of hypoid gear; Finally, the axial installation deviation of large gear. This deviation will cause the root stress of the gear to slightly increase when the large and small gears are meshed, but the root fatigue stress of the hypoid gear is small when the hypoid gear is meshed, so it has little impact on the overall fatigue life. The contact of hypoid gears can be improved by adjusting the axial installation deviation of large gears without affecting the bending fatigue of hypoid gears.
(2) Comparing the change trend of equivalent fatigue stress of large and small gears, it can be seen that the influence of installation deviation on the large wheel of hypoid gear is greater than that on the small wheel of hypoid gear. For the cross angle deviation, the variation range of fatigue stress of large gear is – 207 ~ 339mpa, and that of small gear is – 150 ~ 239mpa. For offset deviation, the variation range of fatigue stress of large gear is – 96 ~ 120MPa, and that of small gear is – 90 ~ 112mpa. For the axial deviation of the pinion, the variation range of the fatigue stress of the pinion is – 31 ~ 51mpa, and that of the pinion is – 11 ~ 49MPa. For the axial deviation of large gear, the variation range of fatigue stress of large gear is – 12 ~ 79mpa, and that of small gear is – 48 ~ 56mpa.
(3) Compare the distance from the point where the stress of the hypoid gear does not change to the end of the hypoid gear caused by different installation deviations. The distance between the large gear pair and the small gear pair shall be the distance between the large end and the small end. The order from the large to the small is the axial installation deviation g of the large gear, the installation offset distance deviation V of the hypoid gear, the installation intersection angle deviation Gama of the hypoid gear, and the axial installation deviation h of the small gear. The sensitivity of the installation deviation of the hypoid gear pair can be improved by optimizing the position of the point where the stress of the hypoid gear does not change.
