In the software ANSYS / LS-DYNA, the contact stress of the helical gear modified by the above two modification methods is analyzed, and the curve diagrams of the stress change process of the second shaft fourth gear helical gear and the intermediate shaft fourth gear helical gear in the two end supported helical gear model with multiple pairs of teeth meshing after modification are obtained respectively. Finally, the modification results of the two modification methods are compared and analyzed.
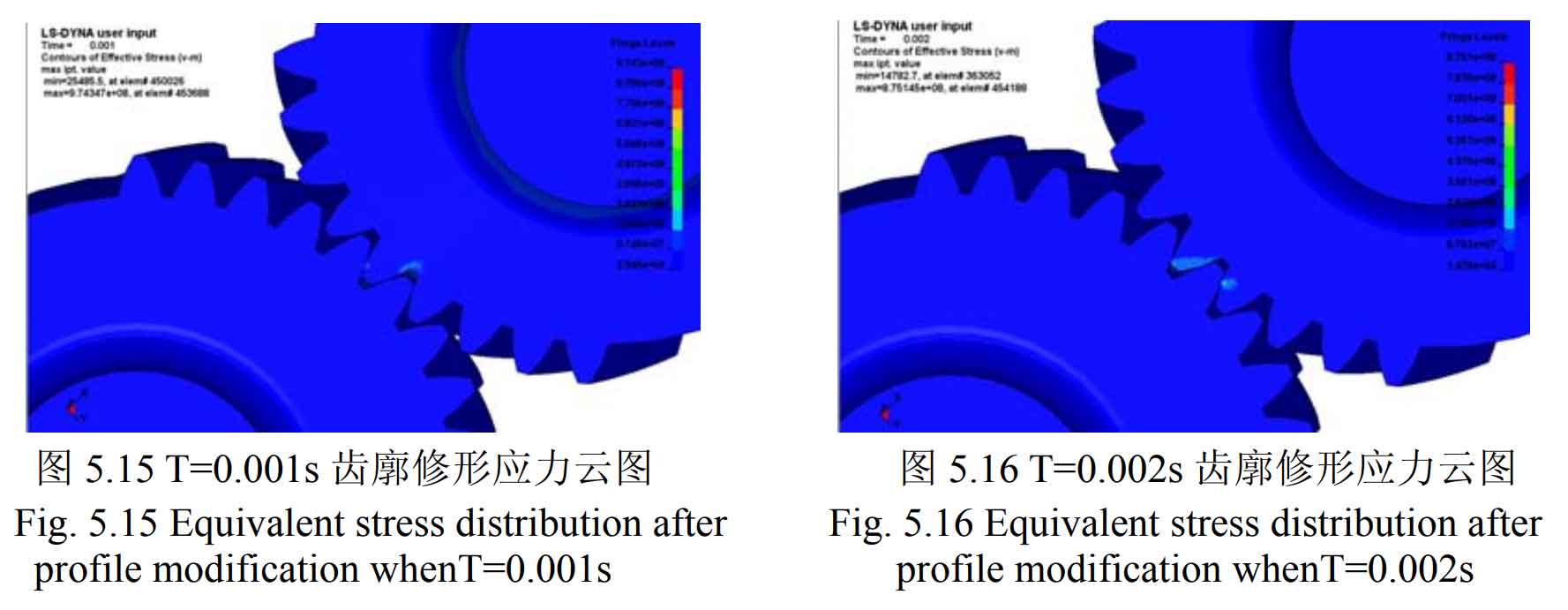
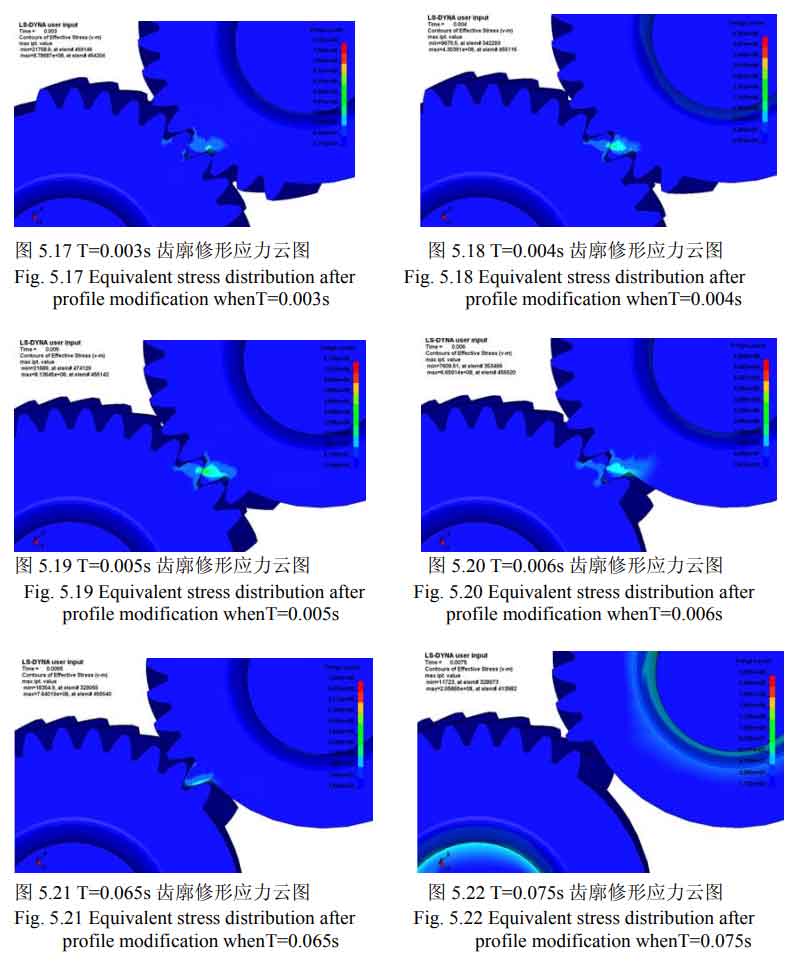
The cloud diagram of the maximum equivalent stress at different times of the second shaft fourth gear helical gear (driven gear) and the intermediate shaft fourth gear helical gear (driving gear) supporting the helical gear model at both ends after tooth profile modification is shown in Figure 1-8.
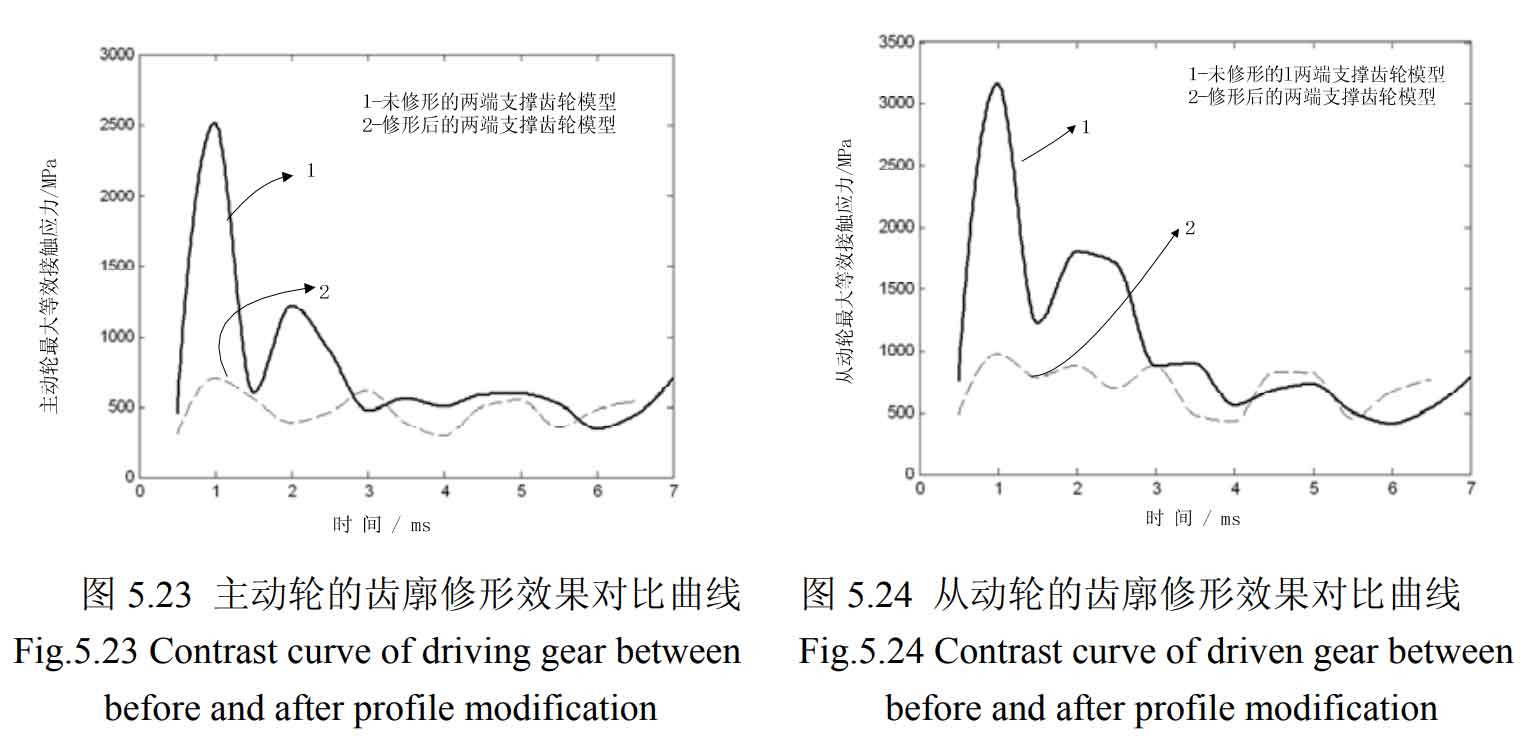
Because there are many frames of dynamic contact simulation animation, in order to facilitate the comparison of stress results, the maximum equivalent stress in each frame animation is the ordinate and the meshing time is the abscissa, which are programmed in MATLAB. The maximum equivalent stress of the second shaft fourth gear helical gear (driven gear) and the intermediate shaft fourth gear helical gear (driving gear) without modification and after tooth profile modification at different times is shown in Figure 9-10 below.
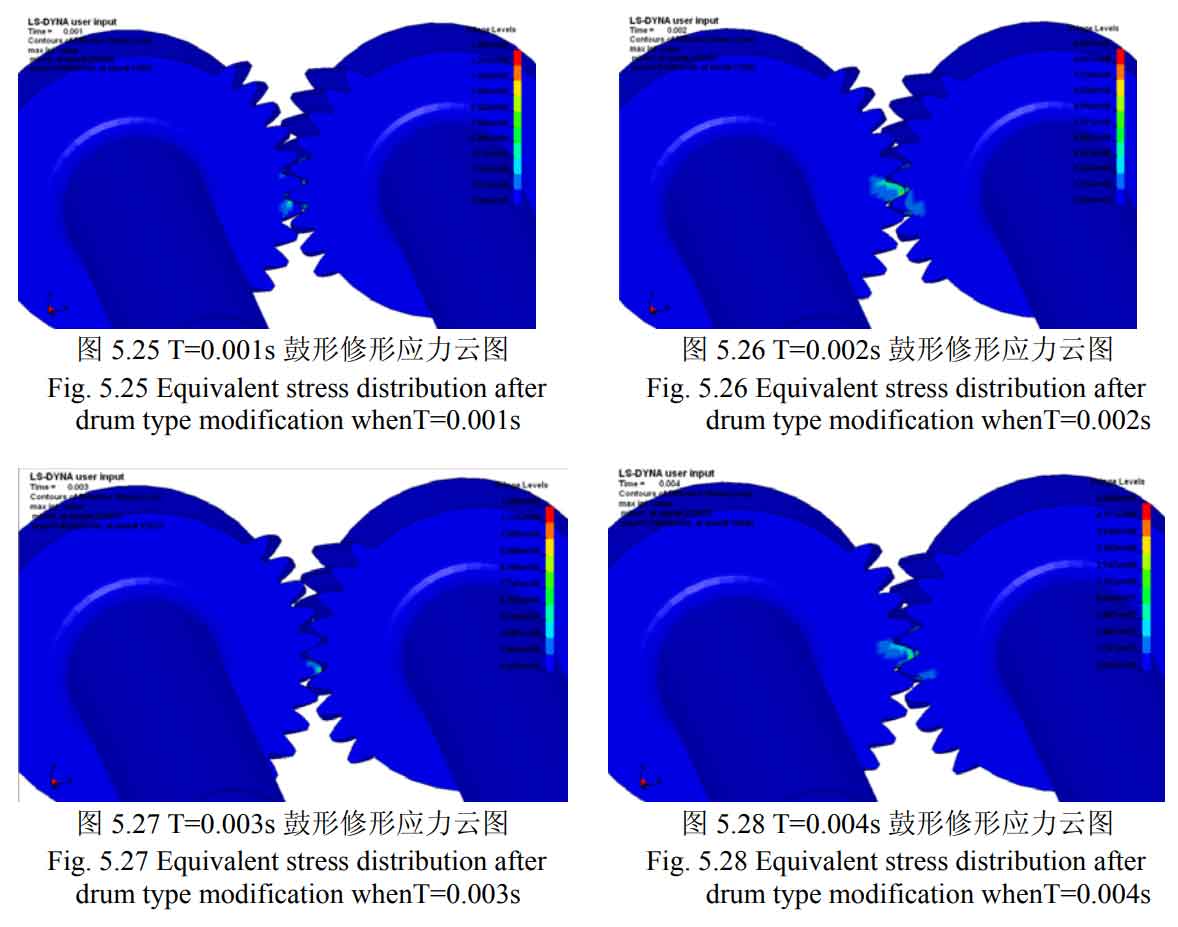
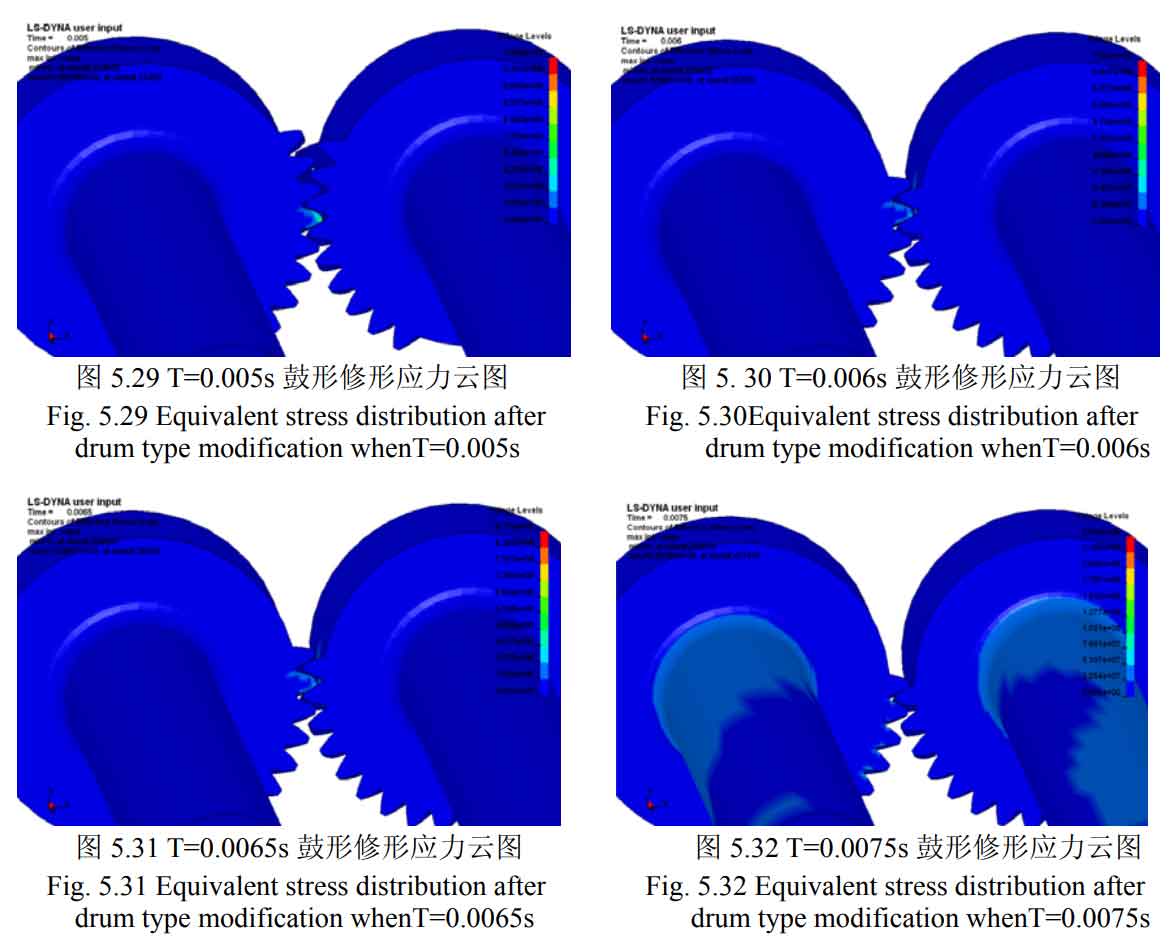
The cloud diagram of the maximum equivalent stress of the second shaft fourth gear helical gear (driven wheel) and the intermediate shaft fourth gear helical gear (driving wheel) supporting the helical gear model at both ends after drum modification at different times is shown in Figure 11-18.
Taking the maximum equivalent stress in each animation frame as the ordinate and the meshing time as the abscissa, the stress nephogram of the second shaft fourth gear helical gear (driven wheel) and the intermediate shaft fourth gear helical gear (driving wheel) at different times after programming in MATLAB is shown in Figure 19-20 below.
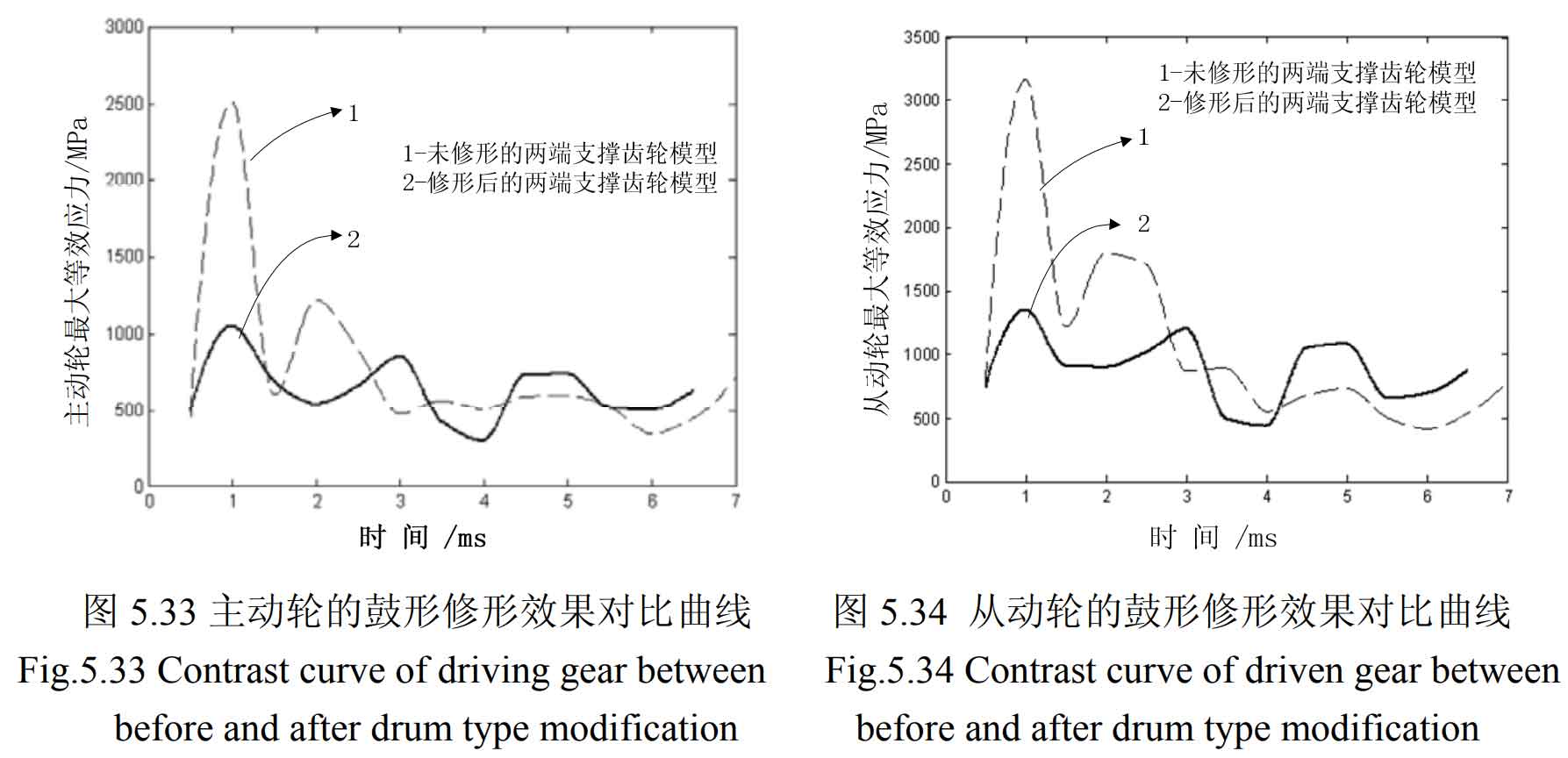
It can be seen from figure 1-20 that after modification, the problem of excessive contact stress of the driving and driven wheels in the meshing process has been significantly improved. No matter the tooth profile modification or tooth direction modification, the serious stress concentration at the sharp corners of the helical gear teeth has been well improved. The modified helical gear pair does not produce large contact stress in the meshing process, and the stress is evenly distributed and fluctuates gently compared with that before modification. The maximum change of equivalent stress of the main and driven wheels of the modified helical gear pair is shown in the table. It can be seen from the table that the maximum equivalent stress of the main and driven wheels of the helical gear pair after tooth profile modification is reduced from 2511mpa and 3168mpa to 704.6mpa and 974.3mpa respectively, and the stress improvement range is about 70%; The maximum equivalent stress of the main and driven wheels of the helical gear pair after tooth modification is reduced from 2511mpa and 3168mpa to 1052mpa and 1355mpa respectively, and the stress improvement range is about 58%, which meets the requirements of contact strength.
| Maximum equivalent stress of driving wheel / MPa | Maximum equivalent stress of driven wheel / MPa | |
| Unmodified gear model | 2511 | 3168 |
| Tooth profile modification gear model | 704.6 | 974.3 |
| Drum modified gear model | 1052 | 1355 |
The modification effect of tooth profile modification is slightly better than drum modification, because the drum amount selected in drum modification is too small, and the entity repaired in tooth direction has not fully reached the modification amount to improve the ideal state of uniform load distribution in tooth direction. To sum up, involute helical gear pair is easy to produce excessive stress concentration in the meshing process, resulting in sudden change of load, which seriously affects the transmission of helical gear. The modified helical gear can effectively improve the phenomenon of stress concentration, and the helical gear pair will not produce large meshing impact in the meshing process. The transmission of helical gear is more stable, which can significantly improve the contact strength of helical gear, so as to prolong the service life of helical gear.
