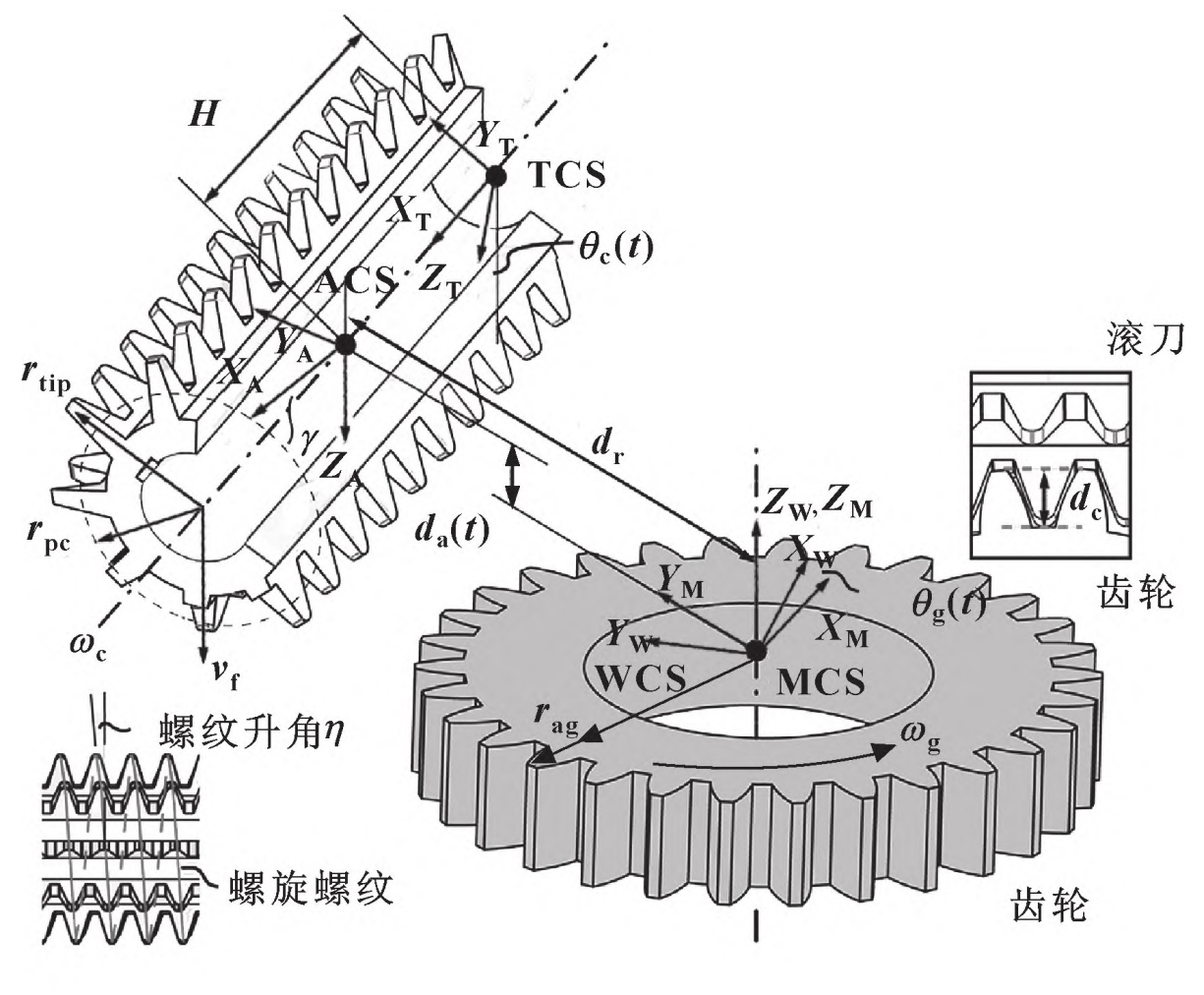
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed simulation method for cylindrical gear machining, several cutting experiments were carried out on Liebherr LC500 CNC hobbing machine tool. The test device is shown in Figure 1. Because the tool and workpiece have undergone a lot of rotation (B1 and C2 axes in Figure 2), it is impractical to use a fixed dynamometer. In order to realize the direct measurement of cutting force instead of relying on the indirect estimation of feed driving current, the Kistler 9123C rotary dynamometer is used. The cutting force measuring device on the CNC gear hobbing machine is shown in Figure 1.
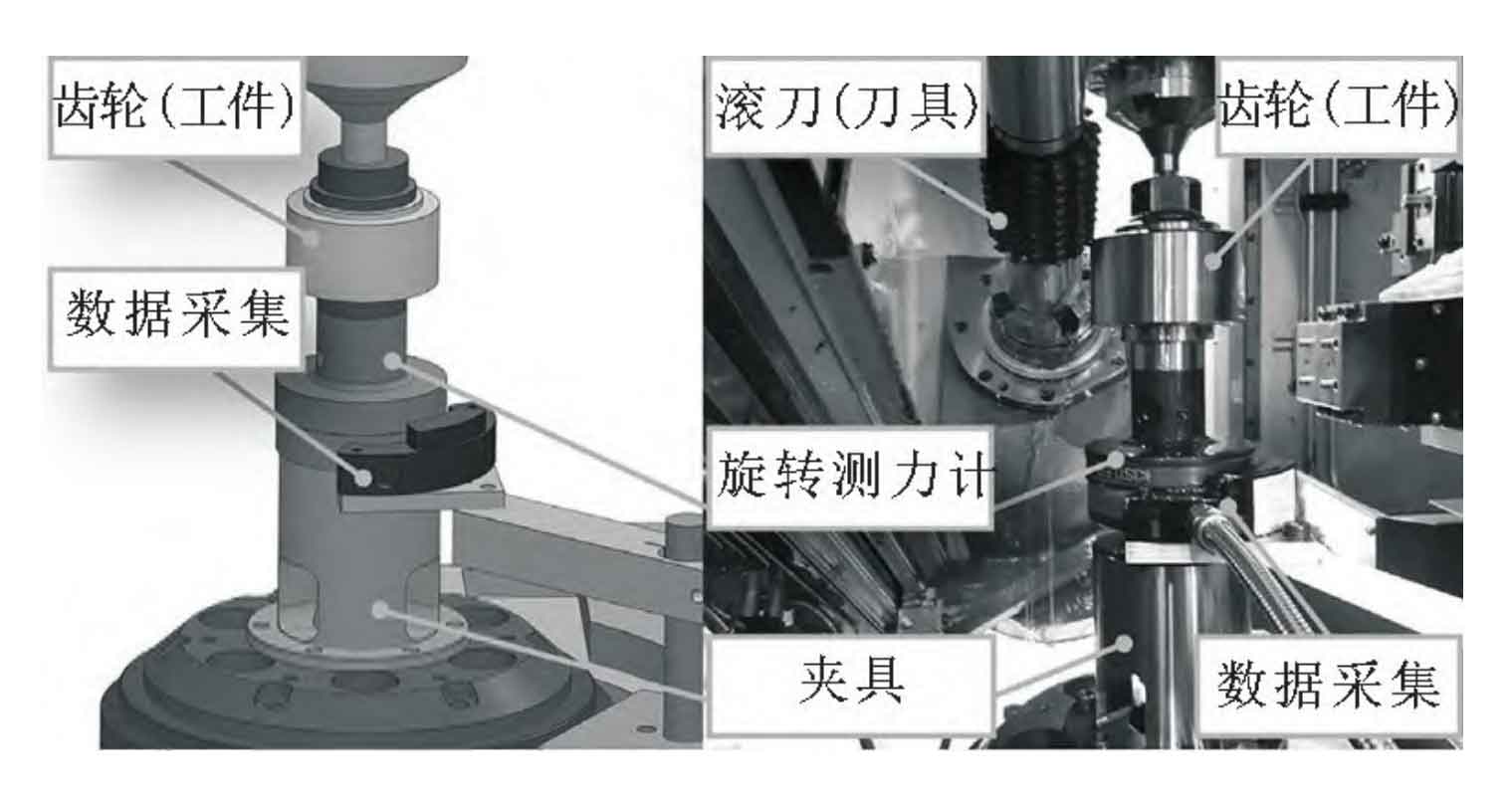
In order to correct the measurement distortion caused by the structural dynamics of the module, the impact hammer test is used to excite the workpiece along the X-Y-Z direction of the MCS, and the frequency response function of the system is determined. When the workpiece is stationary, obtain the corresponding dynamometer output and align the WCS axis and MCS axis. Kalman filter is used to correct the force measurements of MCS in X and Y directions, and then convert them back to WCS for comparison with the simulation results of cylindrical gears. The Kalman filter enables the actual measurement frequency band to reach 450Hz, and corrects most of the distortion caused by resonance.