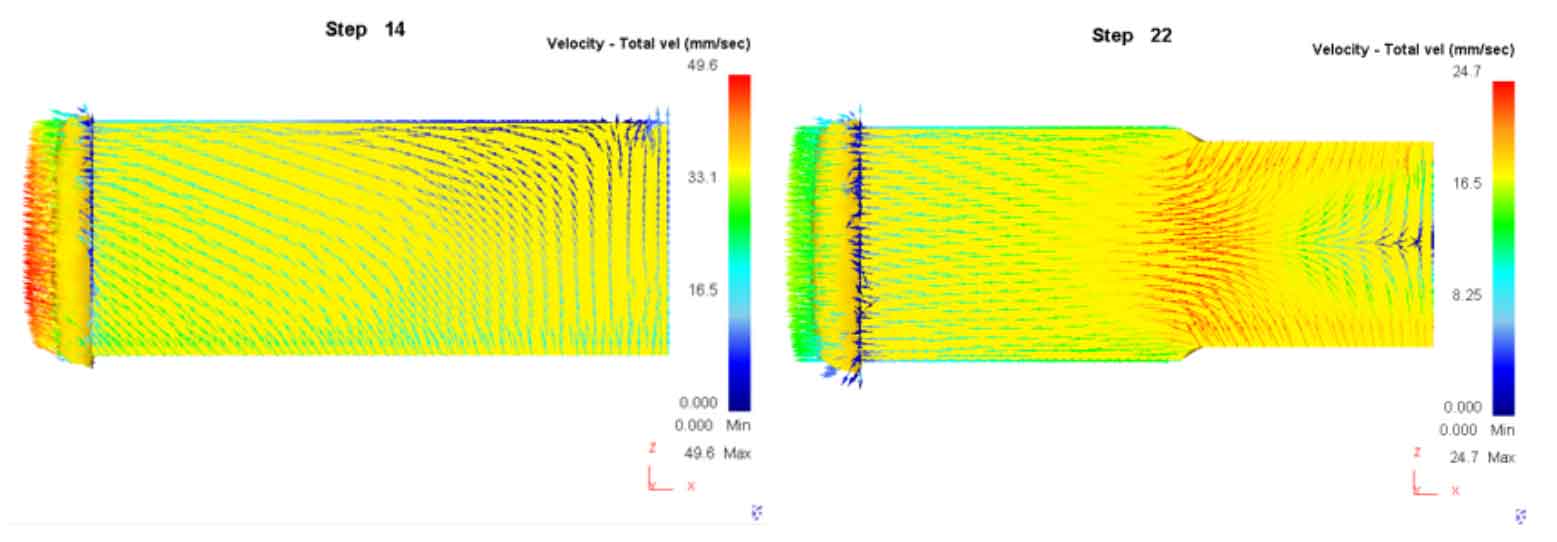
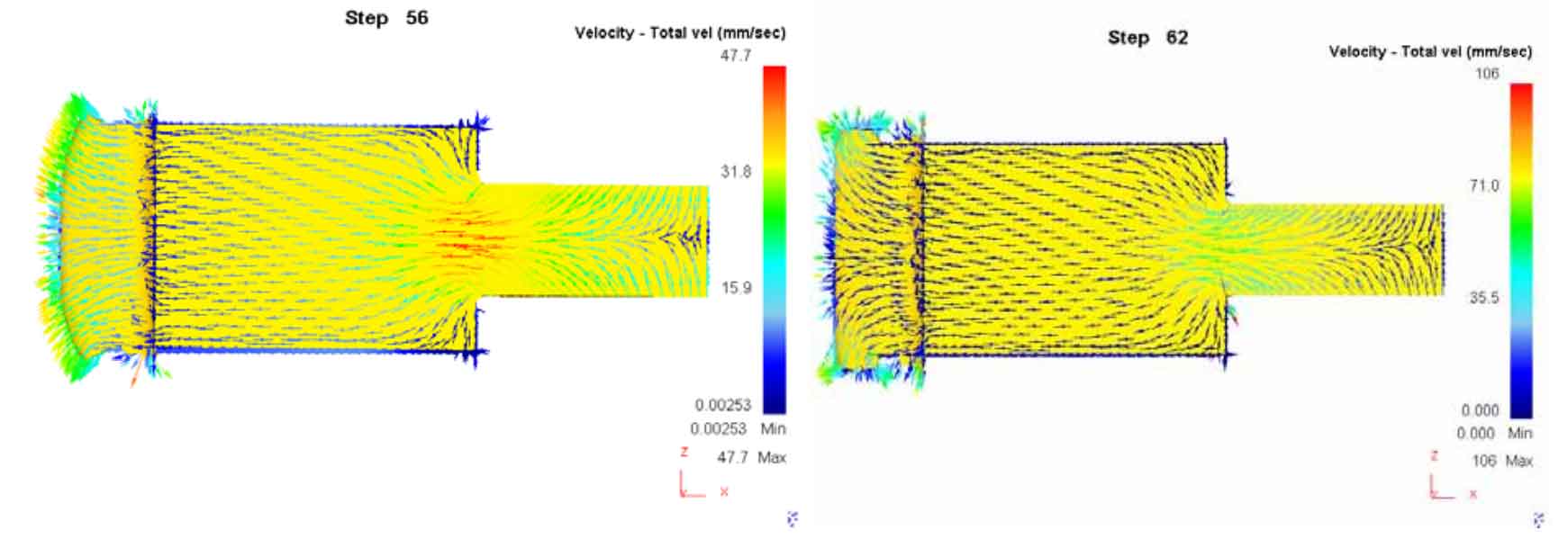
As shown in Figure 1, the distribution of blank velocity field in the forming process after the optimization of spur gear scheme is shown. In the early stage of upsetting and bi-directional extrusion, as shown in Figure A and figure B, the metal flow law is the same as that before optimization. After the middle surface of the tooth top contacts the concave die, the metal flows to the angular gap of the upper and lower tooth top respectively, as shown in Figure C. due to the increase of the free flow surface area of the metal by the shunt groove, the metal flow speed is large. When the metal filling the tooth top crosses the standard line of the end face, stop filling. As shown in Figure D, there is still free flow space for the metal after forming, and the flow speed is large, so as to reduce the forming load.
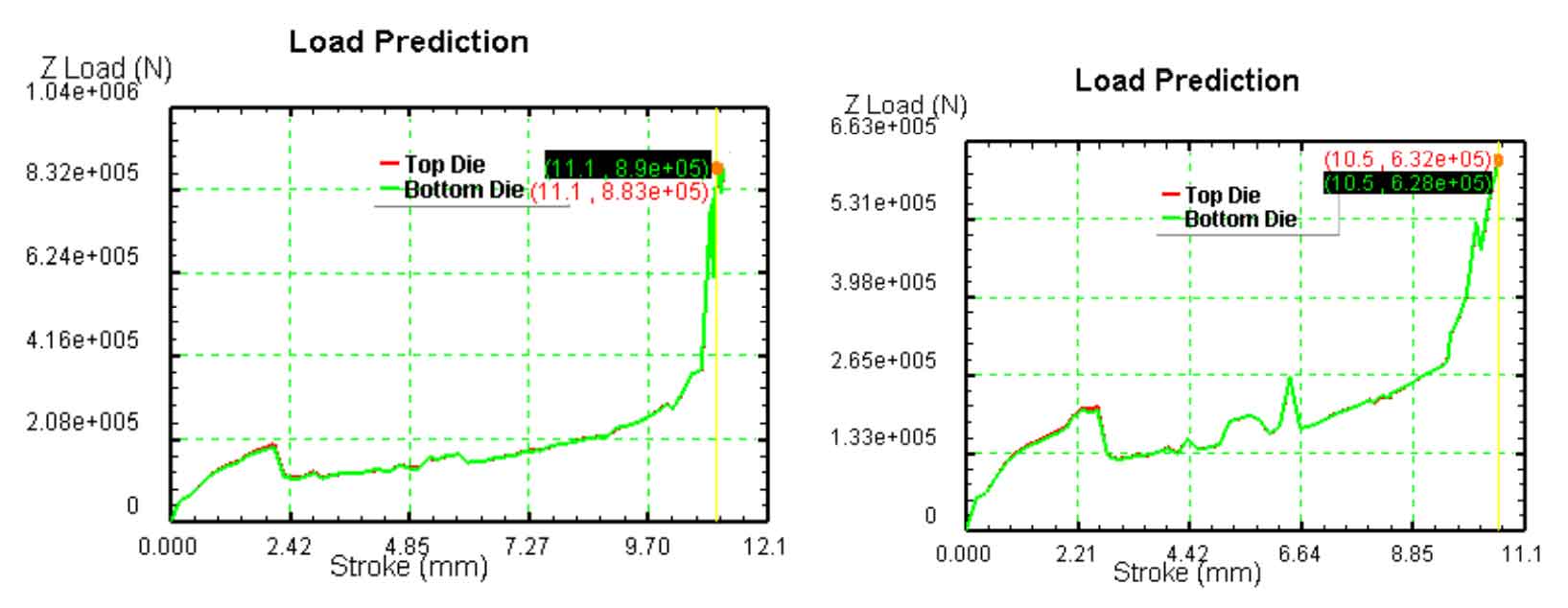
As shown in Figure 2, the stroke load curve of spur gear before and after optimization is shown. Under the same conditions, the stroke load curve after optimization is roughly the same as that before optimization, but the rise of load curve after optimization is slow rather than sharp. The maximum forming load before optimization is 890kn, and the maximum forming load after optimization is 632kn, which is about 30% lower than that before optimization.
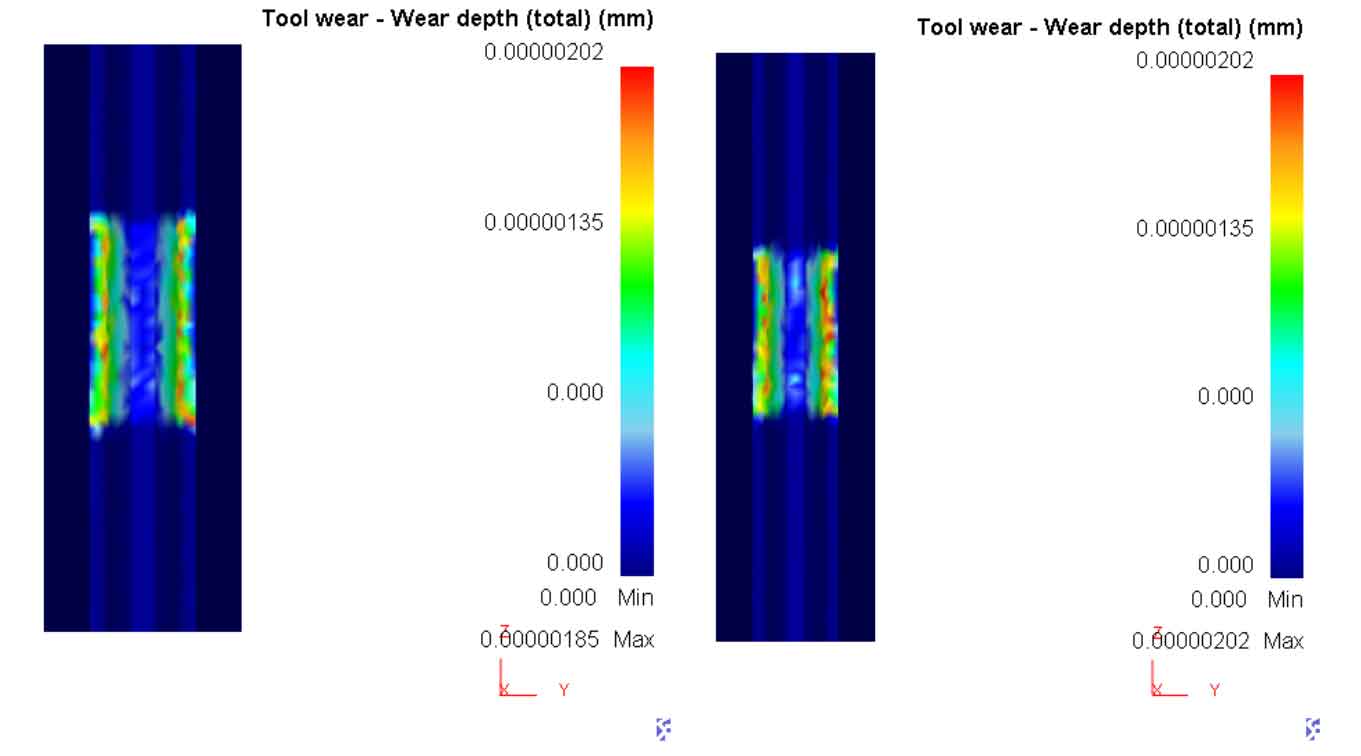
As shown in Figure 3, the die wear diagram of spur gear before and after optimization is shown. Under the same conditions, due to the increase of diversion groove after optimization, the metal flowing into the tooth cavity is more than that before optimization. Due to the effect of friction, the wear amount of female die after optimization is slightly higher than that before optimization.
Setting a diversion groove on the warm forging scheme of spur gear can reduce the forming load and improve the stress of the die, but it is necessary to control the inflow of metal and prevent the increase of die wear. Reasonable lubricant can be considered to reduce the friction between blank and die, so as to reduce the die wear. Water-based graphite lubricant is usually used in the actual warm forging process.