The helical gear transmission system has the advantages of strong load-bearing capacity, smooth transmission, and high transmission efficiency, while excessive contact stress and fatigue on the tooth surface are common forms of gear transmission failure. Establish an external helical gear transmission model using SolidWorks, and conduct transient contact dynamic analysis on the model using Ansys Workbench to obtain the deformation and stress distribution of the external helical gear model meshing.
The helical gear transmission is relatively stable, with minimal impact, vibration, and noise, making it suitable for high-speed, heavy-duty transmission and other situations.The transient dynamic problems of tooth surface meshing contact often attract the attention of gear designers. With the development of finite element calculations and simulation software, using simulation software to obtain mechanical results of models can save costs and time to a certain extent compared to experimental simulations. Therefore, using finite element software for transient contact analysis of gears is of great significance for gear failure.
Encrypt the mesh in the possible meshing area of two helical gears, define the contact surface of the two helical gears, and set the friction coefficient to 0.15. Add ground facing rotating pairs to two helical gears in the load constraint, apply a 3 ° angle to one helical gear, and add a constant torque of 1000N · mm to the ground facing rotating pair of the other gear, with the torque direction consistent with the angle direction.
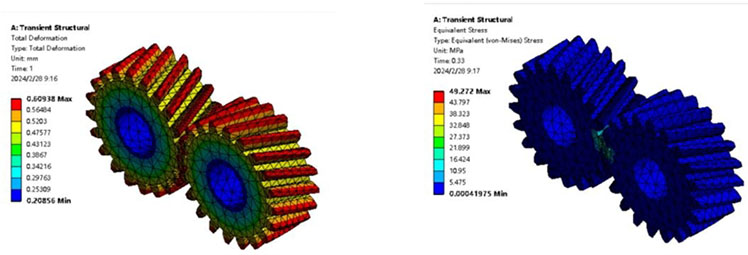
A model of external helical gear transmission was established using SolidWorks and transient meshing simulation was conducted based on Ansys Workbench. Under the condition where one helical gear rotates 3 ° and the other helical gear experiences a constant resistance torque of 1000N · mm, the simulation results show that the maximum stress occurs at the root of the teeth during transient meshing, with a maximum deformation of 0.61mm and a maximum contact stress of 49.27MPa.