Figure 1 shows the meshing diagram of spur gear. Single tooth and double tooth meshing are carried out alternately. The comprehensive stiffness and deformation of single tooth meshing area B-C are small, and the load of double tooth meshing areas A-B and C-D is borne by two pairs of teeth, with large comprehensive stiffness and small deformation. Therefore, in the process of meshing, single and double tooth meshing is carried out alternately, and the deformation also changes periodically. At point a, the deformation of the driving wheel at the tooth root is small, and the deformation of the driven wheel at the tooth top is large, while at point d at the end of meshing, the situation is just the opposite.
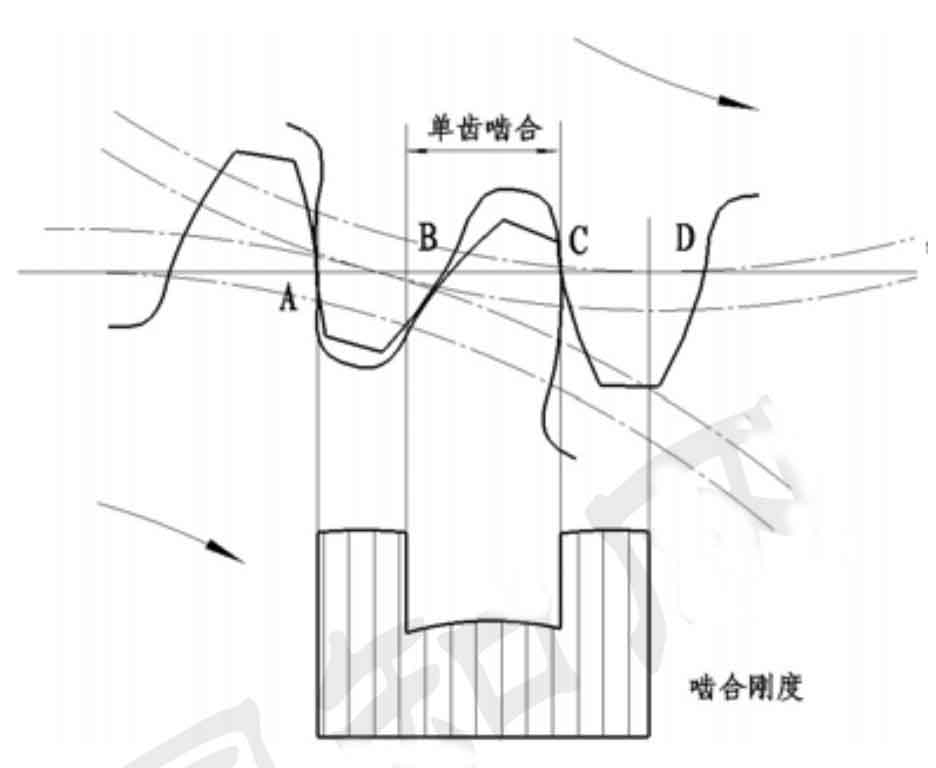
In addition, due to the alternation of single and double teeth, there is an alternating change in the load distribution of the gear teeth, which produces dynamic excitation force and leads to vibration and noise. Spur gear error and loaded elastic deformation are called meshing composite pitch error. According to the correct Meshing Conditions of involute spur gear, the base pitch of driving wheel and driven wheel must be equal, so as to ensure that the sequential meshing between teeth does not interfere with each other. The relationship between the base joint PB1 of the driving wheel and the base joint PB2 of the driven wheel during spur gear meshing can be divided into two cases: PB1 > PB2 and PB1 < PB2, as shown in Figure 2:
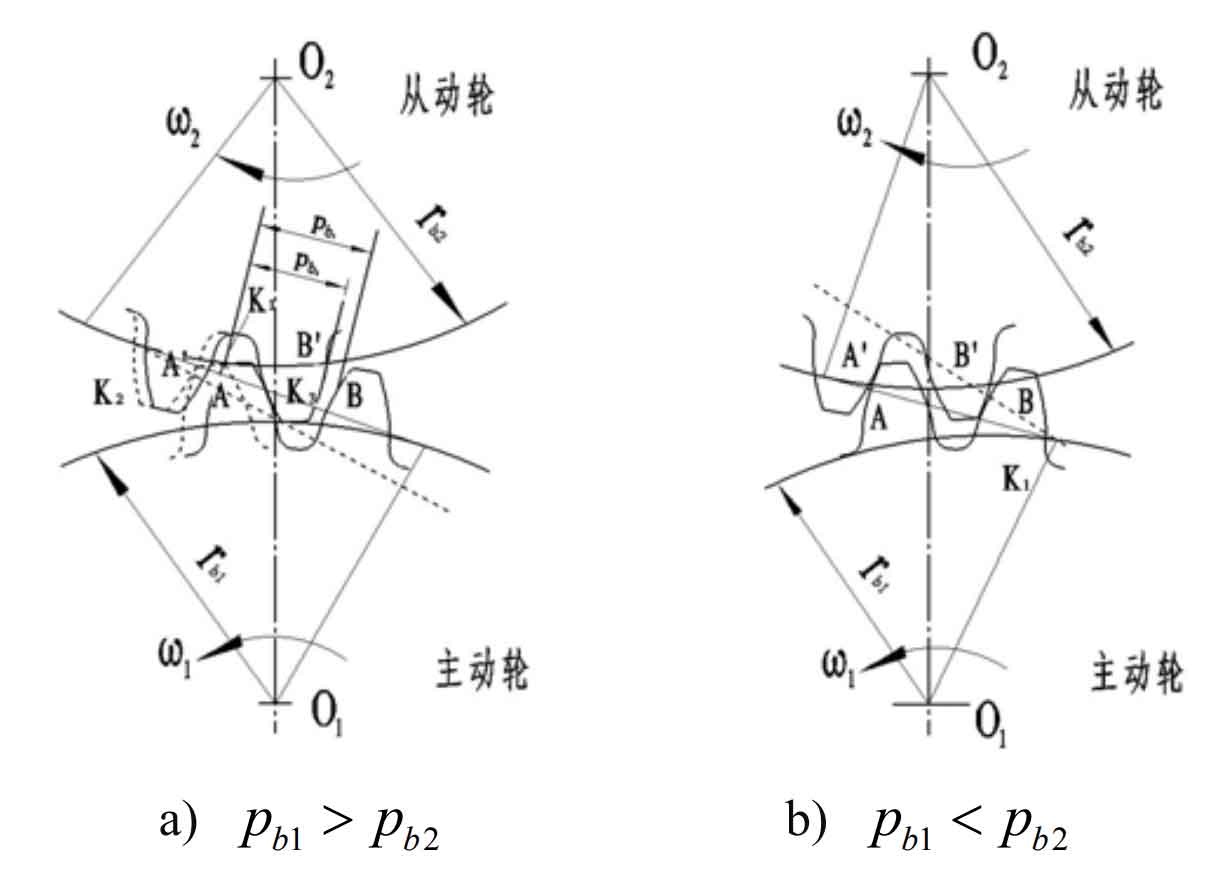
When PB1 > PB2, the previous pair of gear teeth have not finished meshing, and then meshing impact occurs with the latter pair of gear teeth, as shown in Fig. 2 a). When PB1 < PB2, the driven gear teeth enter the meshing in advance, and the meshing impact occurs. As shown in Figure 2 b).
Because the meshing stiffness of spur gears is affected by many factors, such as transmitted load, gear error, tooth profile modification, load distribution, tooth deformation and meshing position, and because the dynamic meshing process of spur gears is completely different from the static meshing process, the meshing of spur gears is affected by the meshing position, vibration speed and displacement, and the meshing stiffness of spur gears is time-varying, During the meshing process of spur gears, the meshing stiffness of spur gears changes periodically, resulting in periodic dynamic meshing force, resulting in vibration excitation of spur gears. Stiffness excitation has a great influence on the system, and it is one of the root causes of the vibration of spur gears in and out of meshing. In addition, from the perspective of kinematics, the change of spur gear meshing stiffness under a certain load will also cause the elastic deformation of gear teeth, and then cause the change of spur gear transmission ratio to cause the vibration of the whole system.
From the theoretical analysis, it can be seen that time-varying meshing stiffness, meshing deformation, load loading mode and its distribution, tooth profile error and tooth surface friction will affect the vibration and noise of spur gears, and are also important factors affecting the dynamic characteristics of spur gears.
