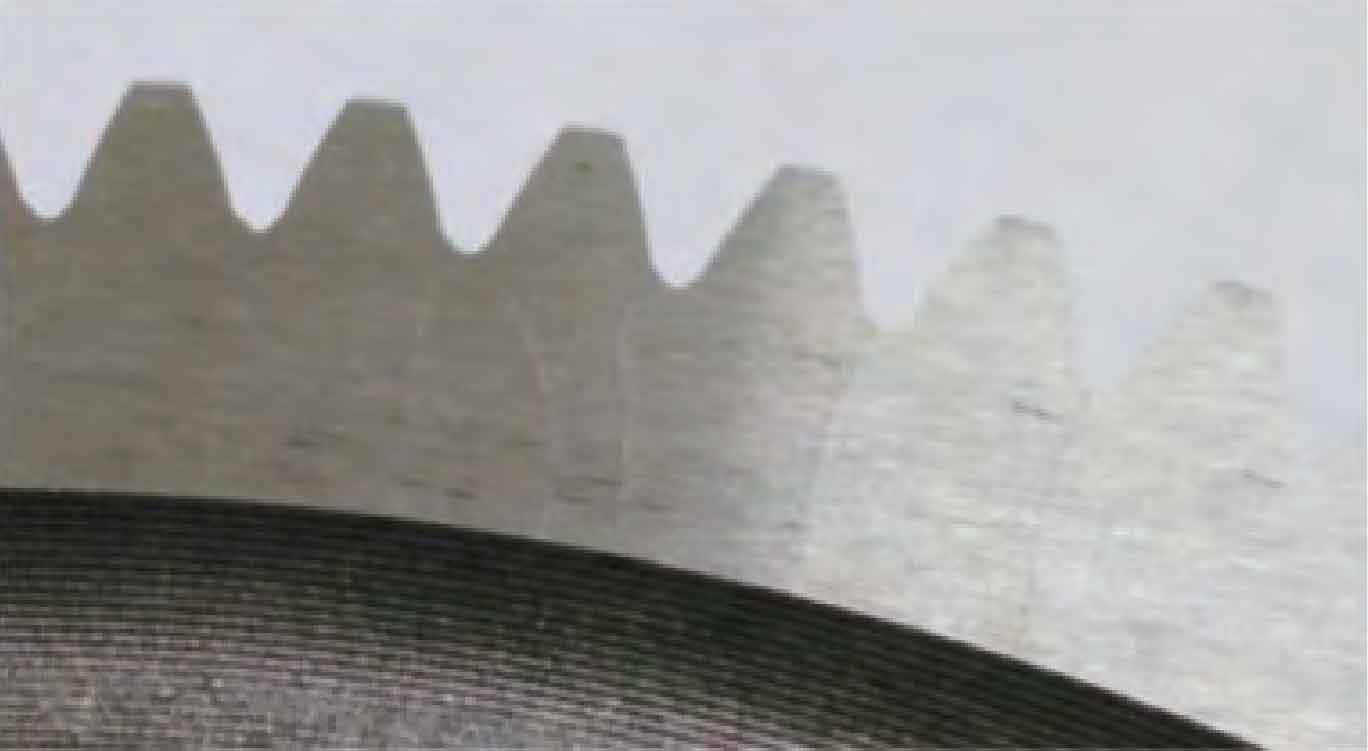
During grinding, a large number of regularly arranged gear grinding cracks often appear on the surface basically perpendicular to the grinding direction. These cracks have become the main defects of grinding.
1.Mechanism and characteristics of gear grinding crack
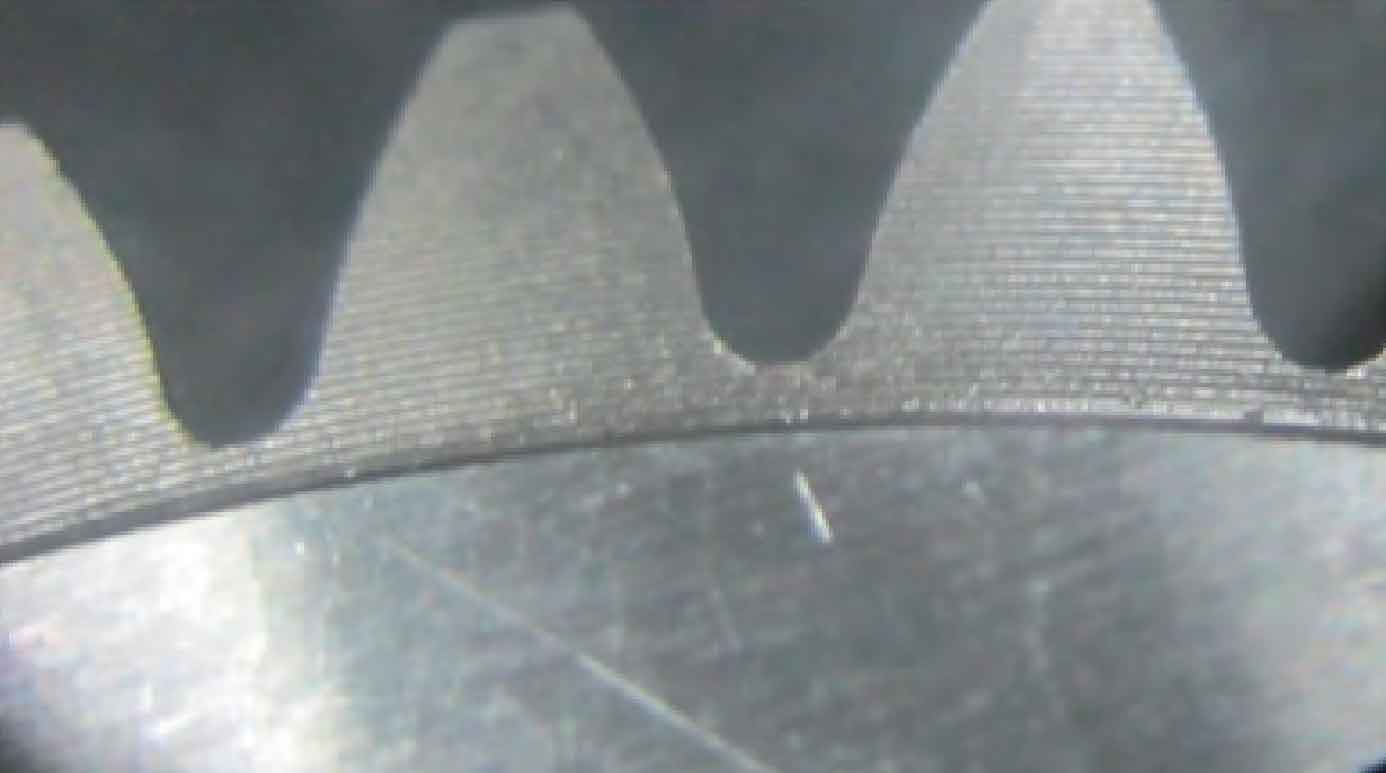
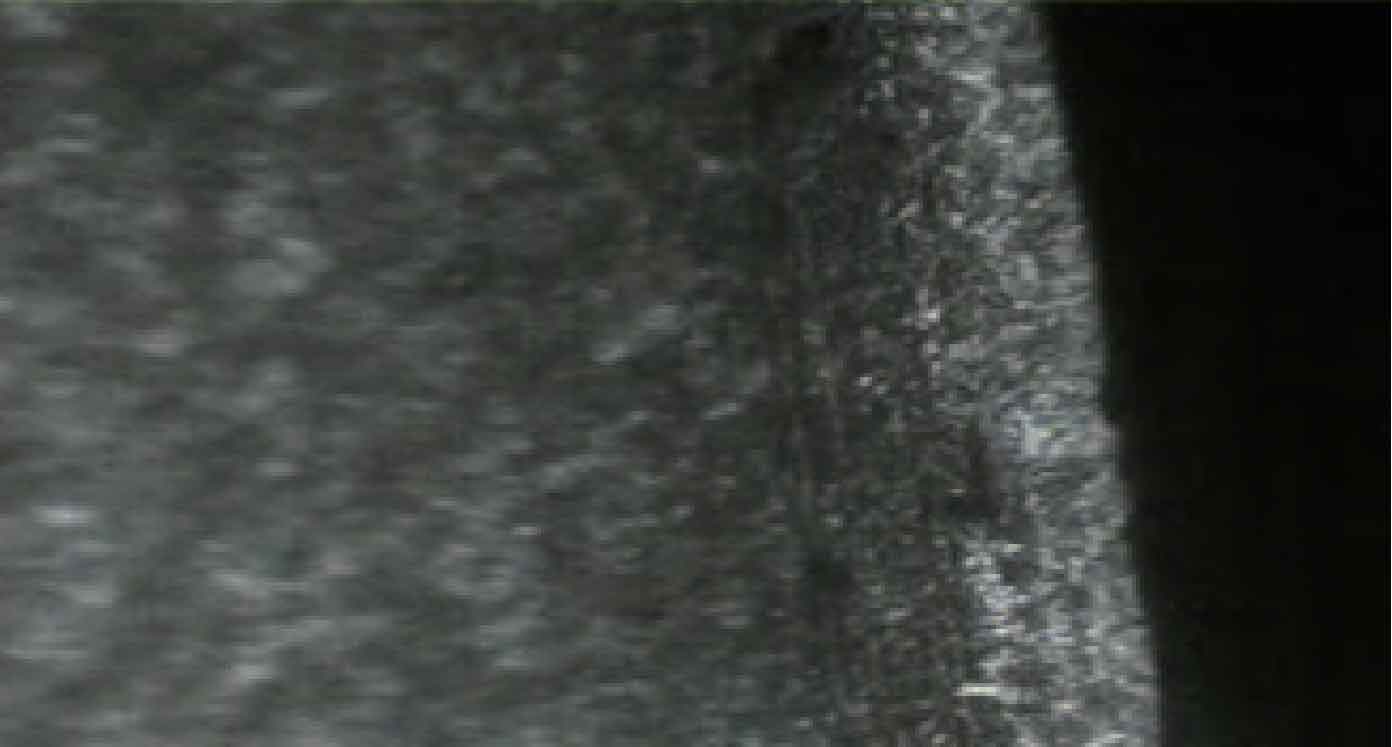
There are two main manifestations of gear grinding crack fault, one is in thin line shape (see Fig. 1), the other is in network shape (crack) (see Fig. 2). Both gear grinding cracks are perpendicular to the grinding direction.
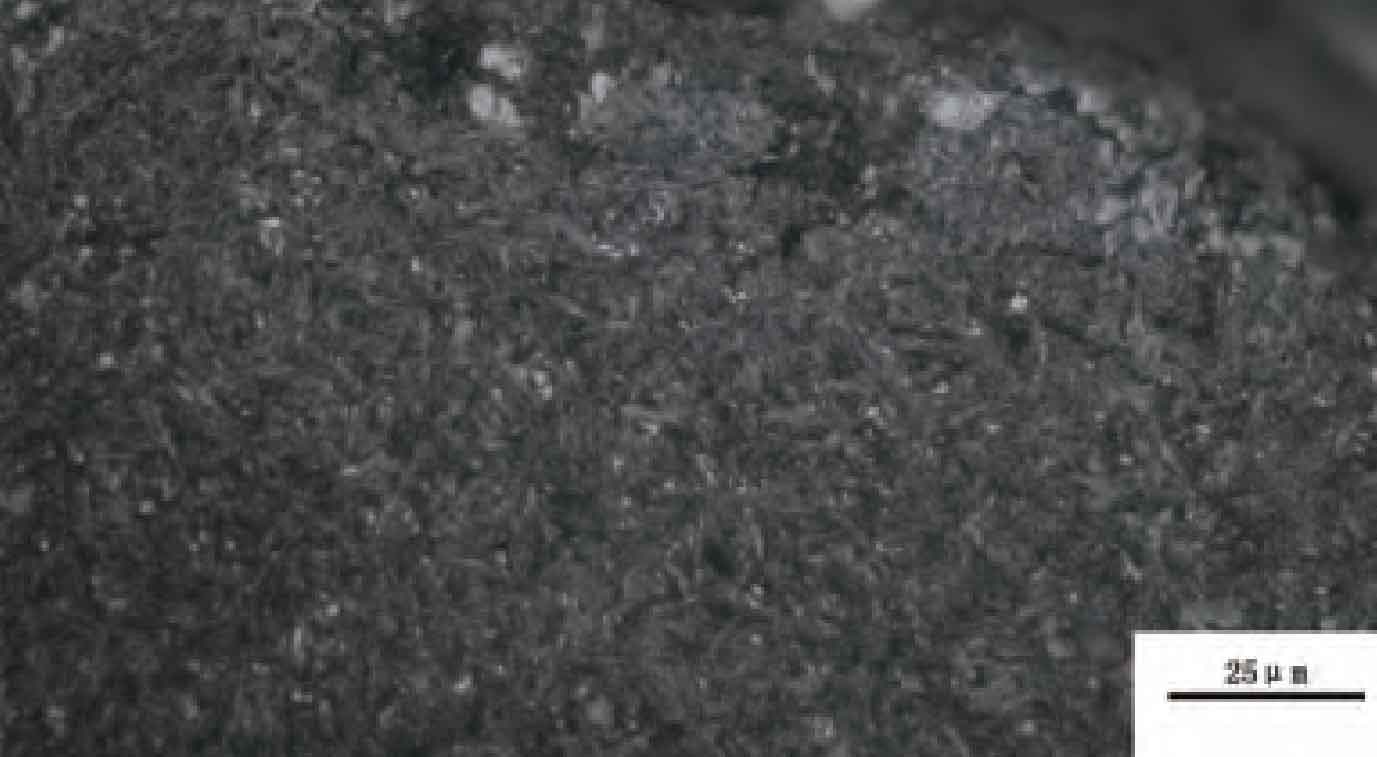
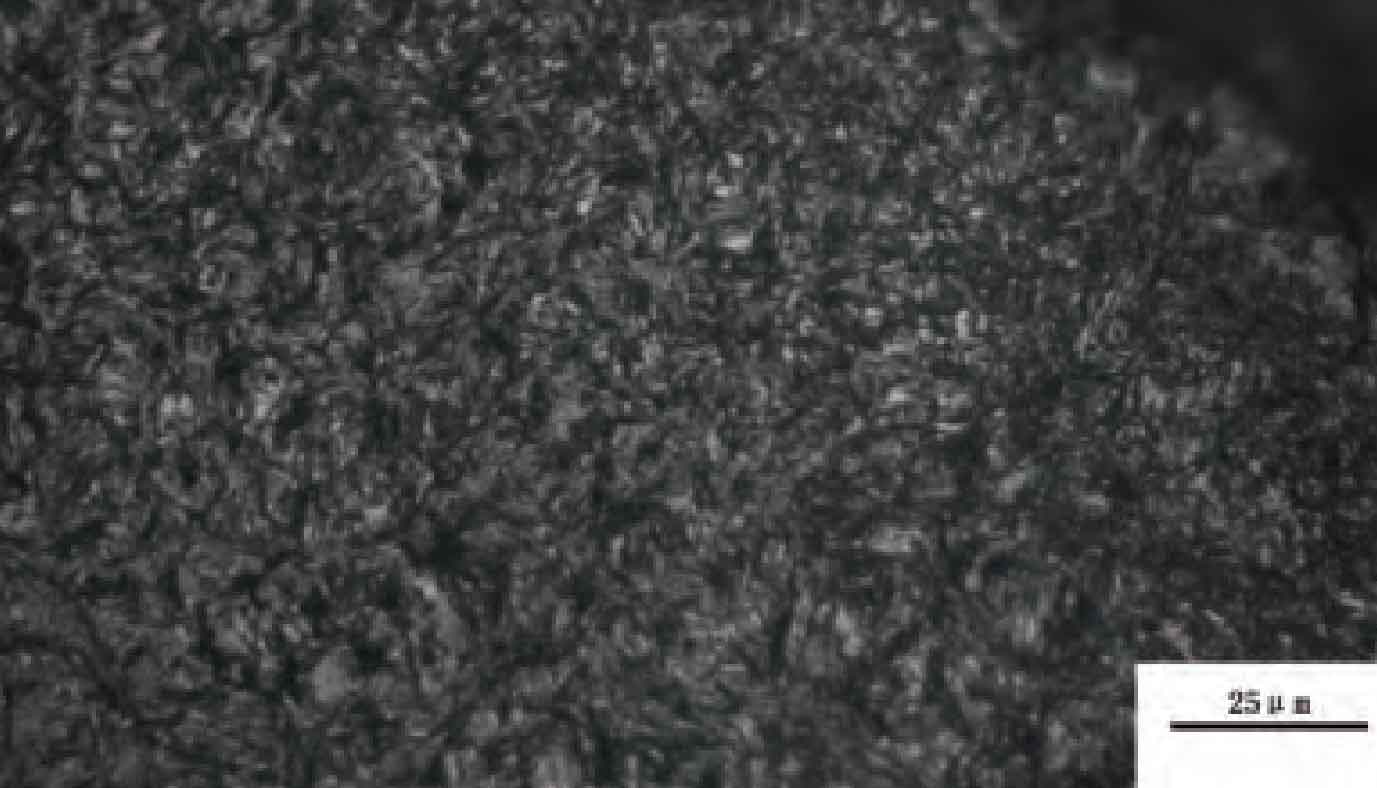
The gear material is 20CrMnTi. After carburizing and quenching treatment, the surface hardness is required to be 59 ~ 63hrc, the core hardness is required to be 30 ~ 43hrc, and the depth of hardened layer is 0.6 ~ 0.9mm (550hv3). Its metallographic structure shall meet the requirements of metallographic inspection of Automobile Carburized Gear QC / t262-1999. It is inspected under 400 times magnification. The carbide of constant mesh gear is 1 ~ 5, and the residual austenite and martensite are 1 ~ 5, The maximum depth of non martensitic structure on the surface shall not exceed 0.02mm. Figure 3 shows the metallographic structure of the tooth top, and Figure 4 shows the metallographic structure of the pitch circle.
The carbide grade is determined according to its shape, quantity, size and distribution. The grade of retained austenite is determined according to its content, and the grade of martensite is determined according to its needle size.
Through the metallographic and performance analysis of the fault gear, the metallographic structure and heat treatment hardness of the gear meet the requirements. For the metallographic structure of the tooth surface, the normal microstructure should be tempered martensite, carbide and a small amount of residual austenite. However, from the metallographic diagram of the cracked gear, the white area on the surface layer is quenched martensite and tempered troostite, which is an abnormal structure, as shown in Figure 5.
From the analysis of its morphological characteristics, it should be the surface burn caused by excessive local grinding feed and poor cooling during gear grinding. The tempered troostite should be caused by the temperature rise of the original tempered martensite zone caused by the inward transfer of friction heat. Through analysis, the grinding crack of the gear is mainly caused by a large amount of grinding heat generated in the process of surface grinding. The significant increase of tissue stress and thermal stress in this area is the main reason for the crack of the gear end face.
The gear grinding crack is fine and shallow. The direction of the crack is roughly perpendicular to the movement direction of the grinding wheel particles. The number of cracks varies. The depth of the gear grinding crack is generally 0.05 ~ 0.4mm, and some can be up to 0.8mm. There is a return fire color and blue color around the gear grinding crack.
2.Gear grinding crack fault test verification
The root cause of gear grinding crack is grinding heat. Combined with the actual production situation, from the six aspects of human, machine, material, method, ring and measurement, there are three main reasons for gear grinding crack: one is insufficient cooling of the machine tool, the other is not operated in strict accordance with the process parameters, and the third is the reduction of product surface temperature due to seasonal changes.
In order to verify the fault causes, combined tests are carried out from three aspects: cooling conditions, whether to add secondary tempering, process parameters and workpiece temperature difference.
(1) The effect of cooling conditions on gear grinding cracks is verified. The test shows that when the workpiece in the same state has the same feed rate and insufficient cooling, the frequency of gear grinding cracks is high, the number of gear grinding cracks is large, the length is greater than 5mm and the depth is 0.2mm; When the cooling is sufficient, there is no crack.
(2) The effect of tempering process on gear grinding crack is verified. The test shows that the probability of gear grinding crack of twice tempered workpiece is lower than that of once tempered workpiece.
(3) Verification of process parameters and workpiece temperature difference to verify the influence of process parameters and workpiece temperature difference on gear grinding crack. The test shows that although the feed rate is increased 24 hours after the workpiece is transferred to the processing workshop, there is still no crack on the workpiece.
Through the above experimental demonstration, it can be concluded that: ① the gear grinding crack is the most serious due to insufficient cooling during grinding. ② When the outdoor temperature is low, the workpiece is transferred to the processing workshop and restored to room temperature for reprocessing, which can reduce the generation of gear grinding cracks. ③ When the workpiece is cooled sufficiently and the workpiece reaches room temperature after secondary tempering, the generation of gear grinding cracks can be reduced.
3.Solutions to gear grinding cracks
(1) In terms of cooling, adjust the flow and direction of machine tool coolant to ensure sufficient cooling.
(2) In terms of process, the secondary tempering process is added, and the grinding feed rate is strictly in accordance with the requirements of 0.02mm/stroke in the operation instruction.
(3) In terms of ambient temperature, ensure that the workpiece surface temperature reaches room temperature before processing.
Through the combination of different causes and fault reproduction test of gear grinding cracks, it is analyzed that the main cause of cracks is caused by a large amount of grinding heat in the process of surface grinding. Combined with the production practice, the occurrence of gear grinding cracks can be effectively reduced by sufficient cooling and adding secondary tempering process.