The spiral bevel gear plays the role of transmitting power and changing speed in the working process. There are rolling and sliding between the meshing tooth surfaces, and the root of the tooth is also affected by pulsating or alternating bending. Under the action of all kinds of stress caused by this, the gear will be broken, glued, fatigued and worn. The main stresses causing gear failure are friction, contact stress and bending stress. According to the form and cause of gear failure, the following aspects should be considered in the selection of gear material and heat treatment method:
The gear surface has enough hardness. The tooth surface is actually uneven, so there will be a lot of local pressure, causing metal plastic deformation or embedded in the relative surface, leading to metal direct contact and adhesion. When the meshing tooth surface is relatively sliding, there will be friction. Tooth surface wear is the result of mutual friction. The key to reduce this kind of wear is to improve the plastic resistance of the tooth surface, that is, to improve the hardness of the tooth surface. Improving the hardness of the tooth surface can also improve the contact state of the tooth surface, so as to improve the anti fatigue ability of the tooth surface.
The tooth core should have enough strength and toughness to ensure that the tooth has enough impact resistance under the action of variable load or impact load.
The big and small gears should have a certain hardness difference to improve their scuffing resistance.
Consider material processability and economy. The performance requirements of spiral bevel gear, the spiral bevel gear is the main driving part of the automobile, the driving spiral bevel gear is to transfer the power from the automobile transmission to the driven bevel gear, and the driven bevel gear will transfer the power to the differential. Therefore, on the part structure, the driving spiral bevel gear is a gear shaft, one end is a spline, which is connected with the power output shaft of the transmission, and the other end is a spiral bevel gear; the driven bevel gear is a disc-shaped gear, whose diameter is larger than the driving spiral bevel gear, which plays a deceleration role, and at the same time, some bolt holes are evenly distributed along the circumference to make the driven bevel gear
The wheel is fixed on the differential case by bolts to transmit the power after deceleration to the differential. The driven bevel gear not only has high transmission speed, but also transmits large torque, and bears impact load when loading and braking. The main failure modes of these gears are wear, pitting and fracture. Therefore, the driven spiral bevel gear should meet the following performance requirements: ① good mechanical properties; ② good carburizing and quenching properties; ③ good impact resistance; ④ good core hardness; ⑤ good thermal deformation properties.
Material selection and technical requirements
At present, the materials for spiral bevel gear are 20CrMnTi, 22CrMoH, etc. They are widely used in high-speed, medium or heavy-duty, impact load and friction important parts, and the material cost is relatively low,
The design accuracy of spiral bevel gear is generally based on the gear line speed to determine the working stability accuracy level, and then select the movement accuracy level, contact accuracy level and backlash accuracy level according to the standard. The accuracy grade of spiral bevel gear of medium truck is generally 8-7-7. In CA1092 truck drive axle, the accuracy of driving and driven spiral bevel gear wheel is 8-7-7d. Figure 1 is the part drawing of the driving spiral bevel gear shaft.
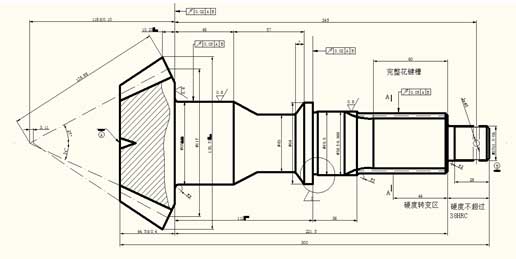
Analysis of technical requirements: the spiral bevel gear will be deformed after carburizing and quenching, among which the tooth deformation can be corrected by grinding or grinding, and the transmission noise of spiral bevel gear can be significantly reduced. This method has been used in car production. In order to make up for the loss of accuracy caused by heat treatment, the accuracy of tooth profile of medium-sized trucks is usually improved. Table 1 shows the involute flower parameters and gear parameters of the driving spiral bevel gear shaft.
Table 1 involute spline parameters and gear parameters of driving spiral bevel gear shaft
|
Involute spline parameters |
Gear parameters |
||
|
Spline tooth profile |
Involute |
Gear |
13 |
|
Module (mm) |
3 |
Module of upper end face of gear dividing circle (mm) |
9 |
|
Tooth number |
14 |
Calculation of engagement angle by normal surface |
20o |
|
Original tooth pressure angle |
20o |
Tooth top height (mm) |
10.26 |
|
Original tooth displacement (mm) |
+1.5 |
Tooth full height (mm) |
16.992 |
|
Pitch circle diameter (mm) |
42 |
Helix angle of gear tooth midpoint |
35o |
|
Thickness of upper arc tooth of gear dividing circle: Theoretical value (mm)
Inspection with passing gauge (mm) Measuring rod inspection (mm) |
5.80 5.82 5.76 |
Rotation direction |
Left |
|
Cutter head diameter (mm) |
Ø228.6(9″) |
||
|
Theoretical arc tooth thickness of upper end face of gear dividing circle (mm) |
16.652 |
||
|
Backlash on the inspection bench after grinding the matched gear (mm) |
0.20~0.35 |
||
|
Involute transition diameter (mm) |
Ø41 |
Working surface roughness of teeth (UM) |
Ra1.6 |
|
Surface roughness of tooth side (UM) |
Ra3.2 |
Grind the teeth as required and mark the gears after matching |
|
