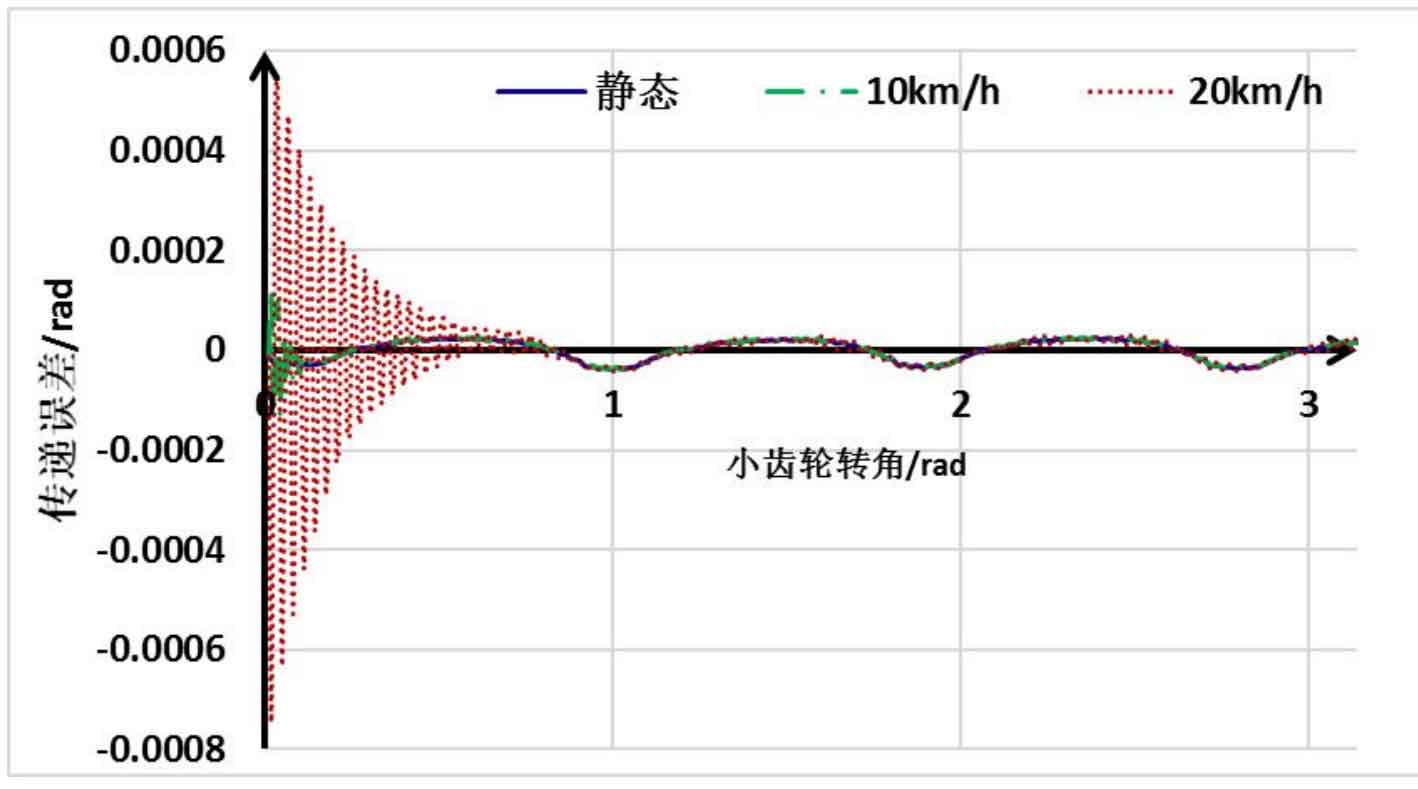
In the dynamic analysis of the hypoid gear, the difference from the static analysis is that the input end of the hypoid gear pinion is loaded with different rotational speeds (this rotational speed corresponds to the vehicle running speed). During the simulation, the load resistance moment of the large wheel of the hypoid gear is the same as that of the static analysis, which is 1000nm. As shown in Fig. 1, the dynamic transmission error and the static transmission error fluctuation are compared. It can be seen that the static transmission error and the dynamic transmission error are the same. There are two main differences between dynamic transmission error and static error. On the one hand, there is obvious oscillation between 0-1 radian. On the other hand, when the rotational speed is different, the rotation angle of the hypoid gear corresponding to the oscillation is also different. This is because the higher the simulated rotational speed of the hypoid gear, the longer the time required for the dynamic simulation to achieve stability. However, after the speed of the simulated gear is stable, the fluctuation trend of the transmission error is consistent. This is because the geometric dimension of hypoid gear has not changed compared with the static analysis step, and the change trend of dynamic transmission error is consistent with the static simulation.
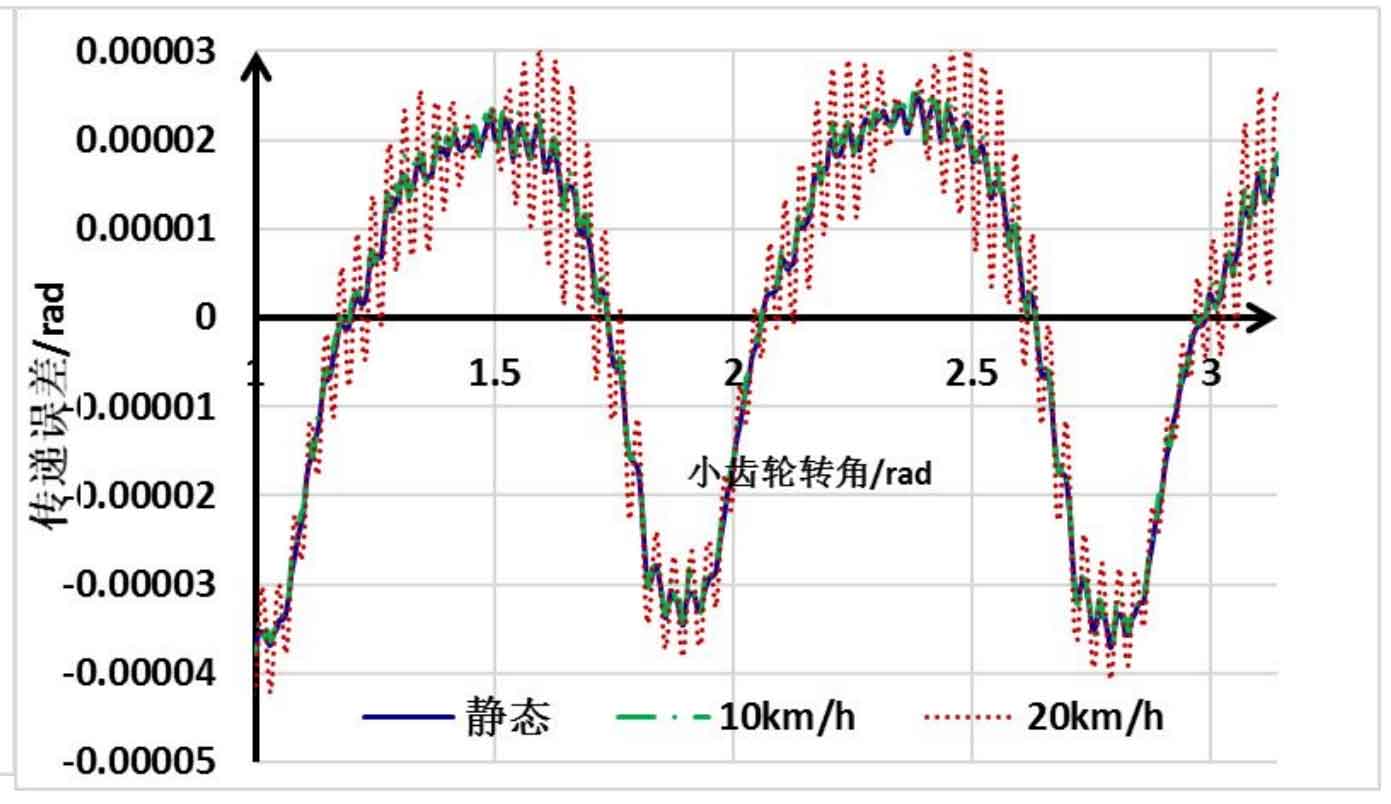
For further comparison, after the simulation is stable, the fluctuation part of the transmission error of the hypoid gear is amplified, as shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen that when the rotation speed of the hypoid gear increases, the corresponding fluctuation of the transmission error slightly increases, but the fluctuation position in the static transmission error will also appear in the dynamic transmission error, but the corresponding peak value will increase, This may be caused by the calculation deviation due to the consideration of dynamic effects in the simulation process.
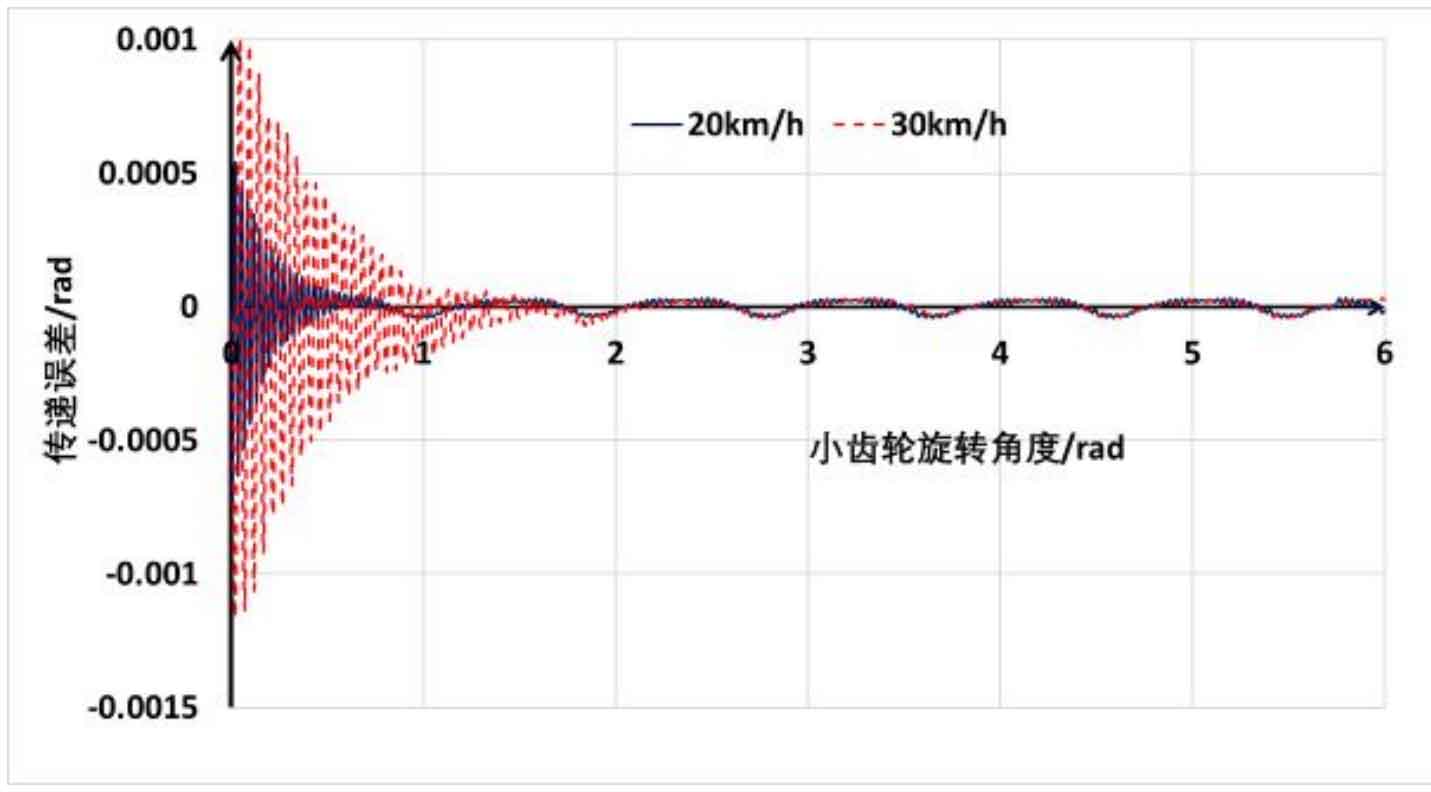
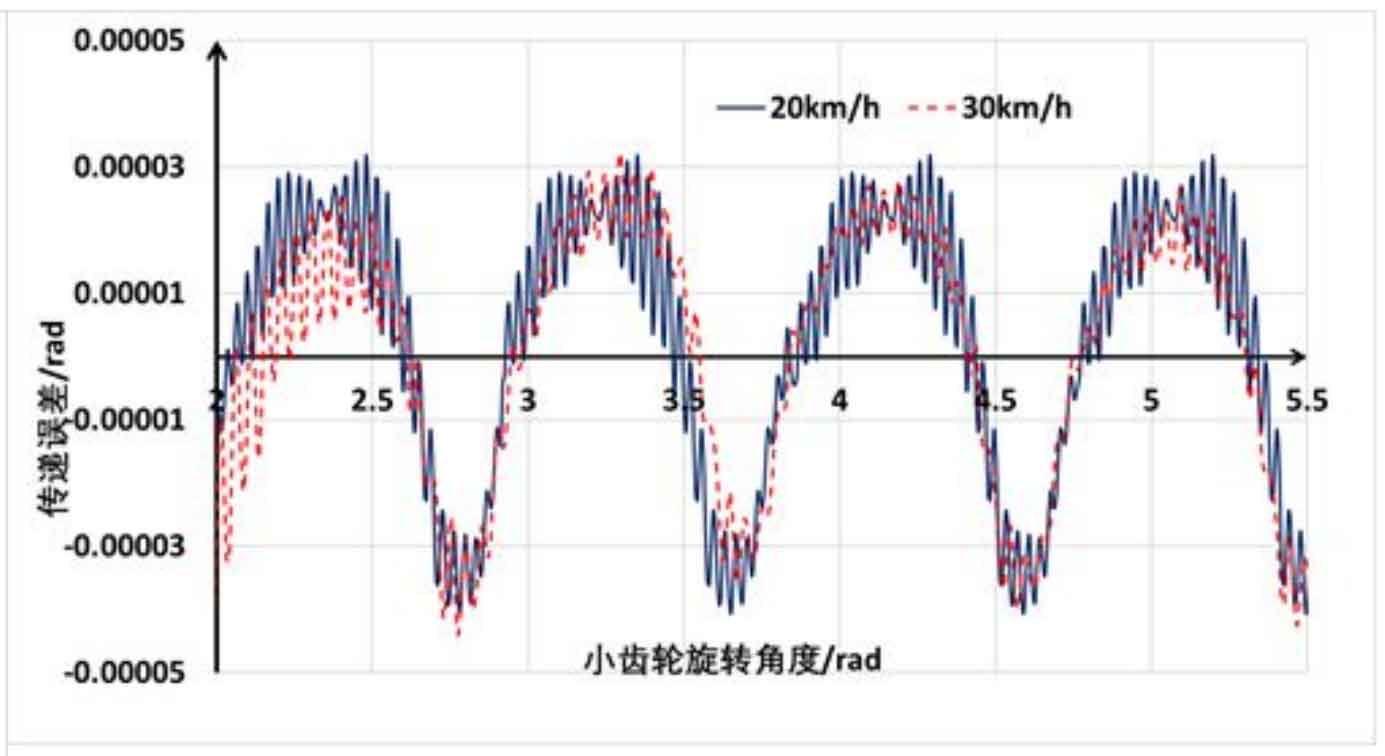
Figure 3 shows the corresponding transmission error fluctuation value when the vehicle is running at 20km / h and 30km / h. It can be seen that the higher the speed is, the longer the rotation angle of the corresponding hypoid gear pinion is when the simulation is stable. However, when the simulation is stable, The fluctuation trend of transmission error is basically the same, which again shows that the fluctuation of dynamic transmission error is not caused by the dynamic effect of hypoid gear. This is also the same as the predicted trend. The comparison results show that the dynamic effect has little influence on the meshing of hypoid gears, which is consistent with the research results. When the influence of factors such as support stiffness, bearing stiffness, input and output load fluctuation of the drive axle hypoid gears is not considered, the dynamic transmission error and static transmission error of hypoid gears are basically the same.