Introduction
Linear conjugate internal meshing gear transmission, also known as straight tooth conjugate internal meshing gear transmission, was first proposed by the Swiss for use in internal meshing gear pumps. In linear conjugate internal meshing gear transmission, the tooth profile of the outer gear is a straight line, while the tooth profile of the inner gear is a conjugate curve. Due to its small tooth profile curvature, high contact strength, and some special meshing characteristics, when used as a gear pair in internal meshing gear pumps, it can achieve the effect of small trapped oil volume, low flow pulsation, and low noise. At present, research on linear conjugate internal meshing at home and abroad is mainly focused on the application of its gear pump. As a form of gear transmission, the research on its meshing principle and transmission performance is very insufficient, and there is still no complete standard for calculating tooth profile parameters. Therefore, its application scope is limited, and research on related meshing theories is also very rare.gear transmission In recent years, due to the gradual recognition of the performance of linear conjugate internal meshing teeth by the industry and their promotion and application in emerging technologies such as servo hydraulic systems, their product research and performance improvement have also been valued by enterprises , which has driven in-depth research on this special gear transmission. Many scholars have also begun to explore the application value of linear conjugate internal meshing gear pairs in the field of mechanical power transmission. This article analyzes the meshing process and tooth profile parameters of a linear conjugate internal meshing gear pair, defines the basic parameters of the linear tooth profile of the external gear, establishes the tooth profile coordinate equation, and systematically analyzes the meshing limit point, pressure angle, meshing line, linear conjugate internal meshing gear transmission and its overlap on the tooth profile. gear transmission The relationship between the tooth profile line segment and the corresponding meshing angle is studied, and a tooth profile parameter design method is proposed to ensure continuous transmission conditions. The tooth profile parameter design method and the meshing performance of the linear conjugate internal meshing gear pair are verified through engineering examples, which has certain significance for expanding its application fields.
External gear parameters and tooth profile equations
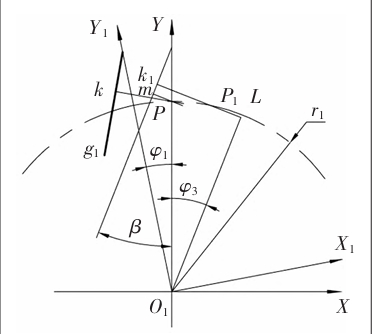
In a linear conjugate internal meshing gear pair, the tooth profile of the outer gear is a symmetrical straight line, with its tooth top and tooth root respectively being a circular arc. The coordinate system O1X1Y1 is established with the center O1 of the outer gear as the origin. The tooth profile equation of the outer gear can be established through multiple geometric parameters, gear transmission such as the tooth profile angle, arc tooth thickness, and the distance between the tooth profile and the gear center. However, from an engineering practical perspective, for linear conjugate internal meshing gear pairs, using a parameter similar to the modulus of an involute gear for geometric calculation of the gear makes it easier for subsequent analysis and research, as well as performance comparison with involute gears. In involute gears, the modulus is related to the indexing circle, and the pressure angle of the tooth profile curve on the indexing circle is specified as the standard value, which is an important feature of the indexing circle of involute gears [9-10]. For standard involute gears, the indexing circle is located in the middle position of the tooth profile meshing area, which can effectively control the range of pressure angle changes during the meshing process and ensure the transmission efficiency of the gear. Similarly, the pressure angle on the straight tooth profile outer gear is also different at each point of the tooth profile, and the pressure angle also affects the transmission performance.gear transmission Following the parameter settings of involute gears, the pressure angle on the indexing circle of the outer gear is defined as the standard pressure angle α, The formula for the half angle of the tooth tip.
Mesh lines and their characteristics
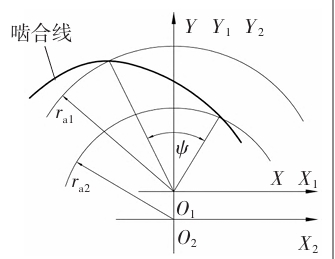
According to the analysis in the previous section, a straight tooth profile external gear can choose any length between the BC points on the tooth profile line as the tooth profile line of the gear, gear transmission forming an internal meshing transmission with the conjugate internal gear. However, under actual operating conditions, continuous transmission requirements should also be considered, and the overlap should not be less than 1. A larger overlap can improve the smoothness of the transmission and increase the load-bearing capacity, but in some special situations, such as internal meshing gear pumps, excessive overlap can cause serious oil trapping. The meshing line is the trajectory of the meshing points in a fixed coordinate frame during the meshing process of a gear pair, which can be solved using the tooth profile normal method. The meshing line can express the meshing characteristics of gear pairs, and can also be used for the calculation of conjugate tooth profiles and the analysis of overlap. gear transmission The overlap of gear transmission is mainly related to the height of the teeth, and the relationship between the overlap of involute gears and the tooth height is approximately proportional because their meshing lines are straight. Therefore, when designing the tooth profile, selecting different sections of involute as the tooth profile, there is basically no significant difference in gear height. However, analysis of the meshing process of linear conjugate internal meshing transmission reveals that the relationship between its overlap and tooth height is completely different from that of involute gears.
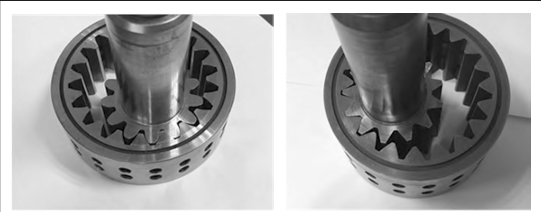
Application examples
In order to verify the research results of this article, a pair of involute internal meshing gear pairs used in an internal meshing gear pump were selected, and the gear parameters were redesigned using linear conjugate internal meshing tooth profiles, while maintaining the same center distance and tooth tip radius of the gears. The parameters of the two gear pairs were compared. In order to ensure interchangeability, the gear circle,gear transmission tooth root circle, and center distance of the two pairs of gear pairs are the same. The calculation results show that the main tooth shape parameters of the two types of gear pairs are similar, but there is a significant difference in the pressure angle variation law during the meshing process.After experimental testing, the gear pair with linear conjugate tooth profile works well in the original involute internal meshing gear pump.
Conclusion
1) In linear conjugate internal meshing gear transmission, the pressure angle of the linear tooth profile external gear depends on the half angle of the tooth tip and the number of teeth; The larger the half angle of the tooth tip, the fewer teeth,gear transmission and the greater the pressure angle; For a given pressure angle, there exists a minimum number of teeth. In addition, the pressure angle decreases with the increase of the meshing point radius, and the minimum pressure angle is equal to the half angle of the tooth tip.
2) There are upper and lower meshing limit points in linear profile external gears,gear transmission and the meshing limit point at the tooth tip may be smaller than the tooth tip circle, resulting in some tooth profiles not participating in meshing and interference phenomena.
3) A straight tooth profile external gear can form an internal meshing transmission with a conjugate internal gear. The tooth profile curve of the internal gear is related to the center distance, and its meshing line is a curve. The degree of curvature of the meshing line increases near the tooth top position of the gear, and the contribution of the tooth height near the tooth top position to the meshing degree is much greater than that of the tooth root part.
The machining of linear conjugate internal meshing gear pairs is not difficult, and the external gears are similar to triangular external splines, which can be machined on milling machines or hobbing machines and ground using spline grinders; gear transmission The machining of internal gears adopts broaching technology for large-scale production, which has high production efficiency and easy accuracy assurance. Gear hobbing can also be used for small-scale machining. It can be foreseen that with the deepening of research on the theory of linear conjugate internal meshing transmission, gear transmission this gear transmission method can not only be better applied in internal meshing gear pumps, but also potentially promoted in fields such as planetary gear transmission.