Introduction
The operation of the ball mill is achieved by the meshing and rotation of the small gear on the transmission end and the large gear on the cylinder. If there are design deviations, manufacturing defects, installation deviations, poor operating environment, and other factors in the gears, it may cause large vibrations during the operation of the ball mill, resulting in gear tooth wear, tooth contact fatigue, gear cracks, gear tooth breakage, and other damage failures, affecting the safety, stability, and long-term operation of the ball mill.
3D modeling

Using UG software for 3D modeling, the appearance geometry and mechanical structure of the ball mill pinion and gear were drawn.
Finite element analysis
Based on the ANSYS software, the dynamic modal analysis of the ball mill pinion and gear is performed to obtain the first six modes of vibration to obtain the maximum variation The first six natural frequencies are calculated to avoid resonance.

Finite element analysis of pinion gear
The first six modes and natural frequencies of the pinion gear






Finite element analysis of large gear
The first six modes and natural frequencies of the large gear
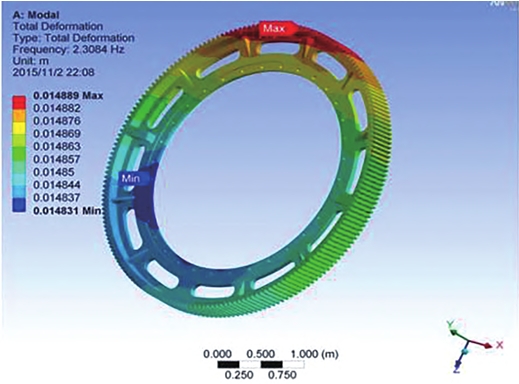
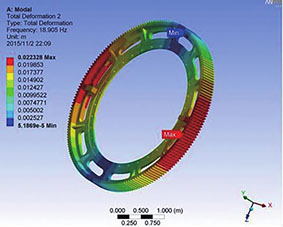


Summary of finite element analysis
The first six modes of vibration and corresponding natural frequencies of the pinion and gear were obtained through finite element analysis. The calculated meshing frequency of the pinion and gear was 296Hz, so the two gears would not resonate due to their natural frequencies and meshing frequencies during operation. From the first six modes of vibration of the pinion and gear, it can be seen that the teeth of the gear are most likely to deform.
Conclusion
During the operation of the ball mill, the large gear is subject to absolute restriction from the small gear of the driving wheel. Due to the fixed speed ratio, this is a speed reduction drive, so it is necessary to increase the speed of the small gear as much as possible within an appropriate range, so that the vibration frequency of the small gear is as small as possible, and the vibration frequency of the large gear is as large as possible, in order to control the vibration frequencies of the small and large gears away from their natural frequencies. At the same time, it is necessary to strengthen regular inspection of the wear degree of the large gear teeth, strengthen maintenance, and collect and analyze the vibration signals of the ball mill in real time.
